Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
FY 2025
Capital Investment Plan
Table of Contents
Major IT Investments .......................................................................................................... 3
Case Management ...................................................................................................................................... 3
Compliance ................................................................................................................................................ 7
Compute ..................................................................................................................................................... 9
Digital Services ........................................................................................................................................ 11
Engagement Channels ............................................................................................................................. 14
Filing and Intake ...................................................................................................................................... 16
Infrastructure Management ...................................................................................................................... 19
Internal Operations .................................................................................................................................. 20
Network Services ..................................................................................................................................... 23
Platforms & Applications ........................................................................................................................ 24
Storage ..................................................................................................................................................... 27
Tax Account Management ....................................................................................................................... 29
User Services ........................................................................................................................................... 31
Major Non-IT Investments ................................................................................................ 34
Criminal Investigation Owned Vehicles .................................................................................................. 34
Leasehold Improvements ......................................................................................................................... 34
Security Equipment ................................................................................................................................. 35
Appendix 1: Legacy Investment Crosswalk to New IT Investment Structure .................. 36
3
Note to Reviewers: IRS re-structured its legacy IT investments from an organizational stand-alone
investments model to a capabilities and platforms based model. FY 2024 and FY 2025 Estimated
Obligations are reported under the new IT infrastructure framework. FY 2023 Actual Obligations are
reported based on the legacy IT infrastructure model (see appendix 1).
Consistent with the corresponding Summary of Capital Investments table, the columns included in the
investment tables below are defined as:
• FY 2023 Actuals – Total actual obligations.
• FY 2024 Estimated Obligations – Anticipated obligations from all budgetary resources (e.g.,
balances from prior years, user fees, and FY 2023 Operating levels).
• FY 2025 Estimated Obligations – Anticipated obligations from all budgetary resources (e.g.,
balances from prior years, user fees, and FY 2025 President’s budget).
Major IT Investments
Case Management
Description:
Case Management includes case initiation, case work (selection, assignment, administration, tracking, and
closure), and case reporting and analytics to resolve a broad range of cases that now require a
combination of IRS business personnel and electronic workflows. This investment covers a cross-cutting
business area comprised of policy, programmatic, and managerial support functions necessary to IRS
operations for cases that could originate in other business areas including data retrieval from systems such
as the Integrated Data Retrieval System.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Case Management
Account Management Services (AMS), Appeals Centralized Database System (ACDS), Audit
Information Management System (AIMS), Automated Insolvency System (AIS), Automated Trust
Fund Recovery (ATFR), Compliance Tools, Criminal Investigation Management Information
System (CIMIS), Enforcement Revenue Information System (ERIS), Enterprise Case Management
(ECM), EP/EO/GE Aims Report Processing Systems (EARP), Integrated Data Retrieval System
(IDRS), Issue and Knowledge Management System (LMSB IMS), LMSB Issue Based Management
Information System (IBMIS), Report Generation Software (RGS) Program, Tax Litigation Counsel
Automated Tracking System (TLCATS), Taxpayer Advocate Management Information System
(TAMIS), TEGE Support Systems (TEGE SS)
*Under the legacy structure, AMS, ECM and IDRS were categorized as Major IT Investments; some, or all their sub-investments are now aligned under Case
Management.
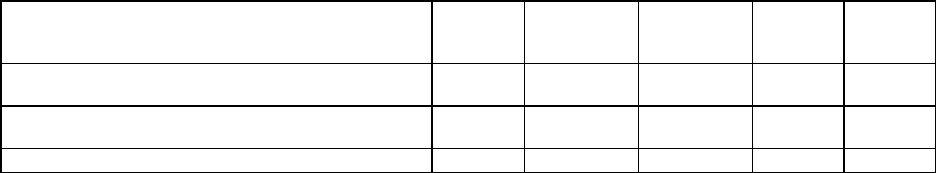
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
310.51
400.52
90.01
28.99%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
75.96
85.78
9.81
12.92%
Total Obligations
0.00
386.48
486.30
99.82
25.83%
4
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
Enterprise Case Management (ECM):
ECM provides an enterprise solution for performing case management functions using a Commercial Off
the Shelf (COTS) platform and common services to improve customer service, automate manual
processes, increase efficiencies, and simplify case management systems operations. ECM helps drive
modernization efforts across the IRS, leading to increased business and IT efficiencies and improved
customer service while enabling the retirement of legacy case management systems/components.
The IRS envisions modernizing and standardizing enterprise-wide case management processes and
systems to provide top quality service to taxpayers. ECM will empower employees to rapidly resolve
cases in a simplified technical environment, designed to drive efficiency and collaboration. The ECM
Program's primary focus is on the Exam Line of Business, with a secondary focus on delivering additional
functionality for current ECM applications and on-boarding additional new users as capacity allows.
The target platform for ECM has been deployed into production and we continue to work with various
business process owners to prepare their individual applications to go live. Continued work to integrate
data and common services and develop applications on the platform will result in most major business
organizations transitioning off their legacy case management systems over time. These business process
deployments demonstrate how ECM will improve business units' case management and better serve their
customers. The adoption and evolution of ECM empowers employees to rapidly resolve cases in a
simplified technical environment, designed to drive efficiency and collaboration.
The anticipated benefits include significant cost reductions and a simplification of maintenance tasks. By
centralizing the enterprise-wide technology platform, case management is streamlined, redundancies are
minimized, and overall cost of ownership decreases. In addition, automation (to include the IDRS
modernization efforts) and readily accessible data (providing a 360-degree view of each taxpayer),
together with standardized business processes, notably reduce the time required to resolve cases. Lastly,
the technology platform enhances taxpayer interactions through the integration of digital services and
self-service options with case management. Thus, it allows for a more dynamic and flexible interaction
experience, making the resolution process more effective and efficient for all parties involved.
Account Management Services (AMS):
The AMS application provides a variety of research and case management tools for approximately
41,000 IRS employees. These entities include a multitude of organizations i.e. TIGTA, Tax Auditors and
all those enjoined with collectively ensuring that the IRS accomplishes its core mission and service to the
taxpayer. The AMS system also provides both large-scale inventory management at the enterprise level
and customized workflow management at the individual case level.
Integrated Data Retrieval System (IDRS):
IDRS is a secure, reliable, flexible, and mission-critical system consisting of databases and programs
supporting IRS employees who are working active tax cases. IDRS manages data retrieved from the Tax
Master Files allowing over 60,000 IRS employees who use it daily to take actions on specific taxpayer
account issues, track statuses and post updates back to the Master Files.
IDRS provides for systemic review of case status, reducing staffing needs and providing consistency in
case control. For example, each time a taxpayer phones IRS, the representative answering the phone uses
IDRS to log the call and answer any questions. Actions taken via IDRS include (but are not limited to):
notice issuance; taxpayer correspondence; installment agreement processing; offers in compromise;
adjustment processing; penalty and interest computations and explanations; credit and debit transfers
among accounts; and research of taxpayer accounts for problem resolution of taxpayer inquiries.
5
Using data analytics, IDRS enables IRS to efficiently evaluate taxpayer data to inform enforcement and
secure legal compliance, both domestically and internationally.
IDRS produces a variety of tax information that facilitates collaboration with various internal and external
partners, including Social Security Administration, Bureau of the Fiscal Service, state and local
governments, and tax practitioners. IDRS is continuously monitored for cost, schedule, and project
performance. IDRS's taxpayer-centered services ensures consistent, efficient service, and helps address
various performance gaps.
Accomplishments and Future Objectives: ECM
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Delivered four new features to Privacy, Governmental Liaison and Disclosure (PGLD) including
form updates, notifications and improved search to support efficient separation processing.
• External Referrals Go-Live enabled the public to electronically submit digital referrals. ECM
External Referrals capability provides the workflow for business operating divisions to review
and route referrals to the appropriate business treatment streams.
• Installed and configured Adobe Experience Manager to support Exam Taxpayer correspondence
via standard Media & Pubs templates.
• Deployed Exam functionality to the Training Environment for Tax Compliance Officers to test
the Exam workflow.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Digitalize case information and establish virtual case folders to improve access to case data
through digital channels.
• Encourage service-wide solutions for streamlined case and workload management processes to
consolidate systems with similar functionality.
• Automate workload allocation to assign the next best case to the next available case worker with
the appropriate permissions and skills.
• Build, configure, and update workflows based on case characteristics throughout the case life
cycle with continuous feedback.
• Support IRA SOP Objective 4.1: Transform core account data and processing, by modernizing
ECM to host all compliance workflows, enabling the decommissioning of legacy applications.
• Host all compliance workflows within ECM, thereby enabling the decommissioning of legacy
applications.
• Subsequent ECM releases in FY 2024 and FY 2025 will focus on delivering additional
capabilities for the exam solution while looking for opportunities to migrate additional business
processes to ECM.
6
Accomplishments and Future Objectives: AMS
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Completed User Interface upgrades and migration to remediate security findings and allows all
AMS to run in native Edge mode especially the Correspondence Imaging Inventories (CII)
component.
• Implement a new Graphical User Interface (GUI) tool that will allow certain business contacts to
make updates to AMS Worksheets and Checklists to free severely limited AMS Application and
Development (AD) resources for other work.
• Migrate AMS from existing in-house Continuous Integration and Continuous Development
(CICD) tools and processes to Enterprise offerings (Jenkins Software Tool, Incident Management
of Record (IMR), Central Software Staging Repository (CSSR).
• Migrated AMS ClearQuest to Engineering Workload Management (EWM), Rational Team
Concert (RTC), and Collaborative Lifecycle Management (CLM).
• Reviewed the possibility of adding CII for business units other than W&I to allow for flexibility
in working taxpayer correspondence digitally.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• AMS will continue to deliver UI upgrades and migration.
• Upgrade current IT Architecture to JAVA 11.
• Upgrade current IT Architecture to Windows 11.
• Implement GUI checklist for tool creation.
• Upgrade COTS products Brava & Documentum if DME funding is approved.
• Modify AMS to allow certain SBSE users to have access to both CSCO and Automated
Collection System Support (ACSS) inventories at the same time if funding is approved.
• Upgrade of AMS servers to RHEL8 to review the possibility of adding Correspondence Imaging
Inventories for business units other than W&I to allow for greater flexibility in managing
taxpayer correspondence digitally.
Accomplishments and Future Objectives: IDRS
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Supported a successful filing season.
• Data at Rest Encryption (DARE) implemented on MSQL CDP Web - All Environments.
• Delivered functionality to Only Allow Alpha or Numeric Characters in SEID Field.
• Clean Energy Act, Update TC971 with AC830 to allow entry of qualifying VIN automobile
purchase. The VIN supplied by dealer and must match VIN on taxpayer’s return.
• Successfully delivered all IDRS IRA program UWR’s.
• All programs for Filing Season 2024 successfully deployed for production on schedule.
• Populated Penalty and Interest Tables for Taxpayer Delinquent Accounts (TDA), Automated
Collections (ACS), and Automated Lien (ALP) notices.
• Interest rate changes requiring an update to program code.
• Adjustment Command Code (ADJ54) implemented changes related to several Unified Work
Requests (UWR's), including those related to the future Legislative Initiatives.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
7
• Planning in progress for transformational initiatives IRS will perform in 2024/2025.
• Planning for defining what IDRS modernization means and defining an IDRS roadmap and spend
plan.
• Populate Penalty and Interest Tables for TDA, Automated Collections (ACS), and Automated
Lien (ALP) notices.
• Deliver all adjustments with respect to command code changes related to UWR's, including
Legislative Initiatives.
• Successfully deliver all IRA program UWRs that require IDRS updates.
• Deliver programs, for Filing Season 2025, for production on schedule.
• Interest rate changes requiring an update to program code.
Compliance
Description:
Compliance includes the collection, examination, appeals, and criminal enforcement functions, with key
activities that include forecasting potential non-compliance issues, performing pre-filing preventive
treatment, case prioritization models and algorithms, performing filing, payment and reporting
compliance actions, and investigating criminal violations of the tax law.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Compliance
Automated Collection System (ACS), Automated Offer in Compromise (AOIC), Automated
Underreporter Program (AUR), Business Masterfile Case Creation Nonfiler Identification Process
(BMF CCNIP), Collection Activity Reports (Statutory Reports) (CARSR), Combined Annual Wage
Reporting Federal Unemployment Tax Act (CAWR FUTA), Compliance Tools, Correspondence
Examination Automation System CPE Unix (CEAS CU), Dependent Data Base (DDB),
Examination Returns Control System (ERCS), Excise Files Information Retrieval Systems
(ExFIRS), Federal Payment Levy Program (FPLP), Information Reporting and Document Matching
(IRDM), Integrated Collection System (ICS), Integrated Production Model (IPM), LMSB Selection
and Workload Classification - Component 2 (SWC C2) - B, Return Review Program (RRP)
*Under the legacy structure, RRP was categorized as Major IT Investment; some, or all sub-investments of RRP are now aligned under Compliance.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
184.85
230.82
45.97
24.87%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
126.71
143.54
16.83
13.29%
Total Obligations
0.00
311.56
374.36
62.81
20.16%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of Compliance includes planning and modeling, anomaly detection, case selection, and
compliance common services that enable taxpayers to realize and meet their tax obligations.
8
The goal is to foster taxpayer compliance by providing tools and resources to promote voluntary
compliance and quick, accurate issue resolutions. Modernization of key compliance
systems expedite detection and resolution of non-compliance, shrinking the tax gap. The IRS
will significantly leverage the Enterprise Data Platform and Advanced Analytics, improving data access,
modeling, and analytics, enabling precise compliance measures, and streamlining the taxpayer
experience.
The benefits include a reduced tax gap through improved identification of non-compliance and
fraud. An integrated anomaly detection system will provide real-time detection, leading to
prompt resolution and an enhanced taxpayer experience. Furthermore, voluntary compliance
will be boosted through strategies like pre-filing nudges, self-service opportunities, and
proactive early interactions with taxpayers. These combined initiatives will improve revenue protection,
recovery, deliver superior outcomes for the IRS, and will improve the overall
taxpayer experience.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Documented and socialized the current state and future vision of compliance systems
and applications through the Examination Case Selection (ECS) and Enterprise Automated
Deployment (EAD) Architecture Transition Strategy and Roadmap
in April-July 2023.
• Completed stakeholder analysis of existing anomaly detection and case selection
application owners to expand the Revenue Production Advisory Board for an
enterprise-wide view across the Business Operating Divisions (BODs) in July 2023
• Engaged with the Transformation & Strategy Office for the Business Capability
Prioritization process initiated in August 2023. The goal is to re-align IT
Modernization Roadmaps and IRA Program planning to the outcomes through
November 2023.
• Confirmed support for EAD/ECS from Procurement and the Enterprise Architecture
and Design Office for acquisitions planning activities through strategy and planning.
• Designed Framework for Compliance System Workshops to be conducted with
technical SMEs starting in June 2023 to validate baseline view and document system
pain points.
• Delivered initial data analysis of IT Workforce Tool (ITWT) 2021 Assessment results
to AD leadership in April 2023.
• Completed draft of Unified Compliance Organization (UCO) Decommissioning Activities Desk
Guide and enhanced
template for Project Decommissioning on June 30, 2023.
• RRP delivered 1040X which implements new requirements to evaluate and associate a
return with up to four types of treatment (both IDT and NIDT).
• Completed Solution Concept for Partnership Compliance Evaluation (PCS
modernization) in coordination with Enterprise Architecture Implemented separate resource
queues for rules processing and extracts so that performance issues when reviewing current day
returns for fraud and IDT do not impact sending prior-day selections of returns for potential fraud
and IDT to downstream systems (i.e., Selection and Analysis Platform (SNAP)/Criminal
Investigation (CI)/ Research, Applied Analytics & Statistics (RAAS)).
• Initiated processing of IMF balance due returns.
• Completed fundamental infrastructure improvements for RRP to rebuild overaged
servers to enable Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8 upgrade and cutover to the new Greenplum
Version 6 platform.

9
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Mobilize resources to focus on high-risk and emerging issues that have not received appropriate
enforcement attention, including enforcement pertaining to digital assets.
• Implement data and research approach to inform and continuously refine compliance coverage
levels needed to promote voluntary compliance.
• Establish centralized compliance planning and strategy function to identify potential high-risk
compliance cases using existing systems and analytics.
• Refine approaches and treatments piloted for large corporate enforcement, high-income and high
wealth enforcement, and in key segments.
• Pilot new approaches and treatments for detection and enforcement of key emerging issues.
• Hire and onboard workforce to achieve compliance coverage rate, including specialists and
experienced hires.
• Train and re-skill workforce with specialized capabilities to address complex and
emerging issues.
• Complete IT Future State Technical Competencies Summary Report for AD:
Compliance Domain workforce.
• Build and execute a corresponding workforce re-skilling action plan leveraging IT Academy and
other training resources.
• Deliver completed Decommissioning Project Plans for Automated Campus Exam
(ACE), Correspondence Examination Automation Support (CEAS) and other legacy Compliance
systems.
• Continue foundational infrastructure updates for RRP RHEL 8 new server migration and RRP
Legacy Component (RRPLC) implementation of 2-factor authentication and SNAP Palantir Data
Connection Agent (PDCA) server upgrade.
• Establish the comprehensive long-term ECS/EAD Modernization Roadmap to establish
timeframes for the disposition of legacy systems as part of Government Accounting Office
(GAO)104719 corrective action activities.
Compute
Description:
Compute Services contains spending for all IRS compute resources, whether physical or cloud-based.
Any serverless/containerized/virtualized compute processes will be included to go along with physical
compute resources. All spending on operating systems will also be reported with this investment.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Compute IRS Main Frames and Servers Services and Support (MSSS)
*Under the legacy structure MSSS was categorized as Major IT Investment; some, or all sub-investments of MSSS are now aligned under Storage, Compute, and
Infrastructure Management.
10
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
6.75
6.75
0.00
0.00%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
383.96
422.40
38.44
10.01%
Total Obligations
0.00
390.71
429.15
38.44
9.84%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment focuses on managing all IRS compute resources. These resources span
from physical servers to cloud-based solutions, and include serverless, containerized, and virtualized
computing systems. This investment also oversees the management of operating systems, essential for the
smooth execution of applications and functionality.
The goal of this investment includes maximizing the efficiency and efficacy of the agency's
computational capabilities. It aims to optimize the usage of compute resources, effectively manage
computing virtualization, and ensure smooth operation of all operating systems. This is aimed towards
empowering the agency's business operations and facilitating efficient data processing and application
functionality.
The benefit of this investment includes bringing about improved efficiency and flexibility by allowing for
a streamlined management of compute resources. It enhances scalability and elasticity with virtualization,
enabling the agency to respond to fluctuating computational demands effectively. Also, the meticulous
management of operating systems ensures a robust and reliable environment for application
functionalities, reducing downtime and maintaining service reliability.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Successfully refreshed the International Business Machine (IBM) mainframe Tax Processing
infrastructure to z/16, which is the latest modern version. The IBM mainframe is the primary host
for critical Tax programs such as CADE2, IMF, and BMF processing. The upgrade increased the
processing performance over the previous system and supports critical application code
transitions from legacy Assembly\Cobol to Java (ITPE).
• Successfully refreshed the Unisys mainframe Tax Processing infrastructure to Unisys Dorado
8590, which is the latest modern version. The Unisys mainframe is the primary host for critical
Tax programs such as IDRS, Generalized Mainline Framework (GMF) and Error Resolution
System (ERS) processing. The upgrade increased the processing performance over the previous
system, which reduced the weekend processing times and will allow the IRS more real time
processing windows.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Transition to cloud and managed service providers where possible.
• Perform continuous monitoring and patching of aged hardware and software assets to mitigate
security risks.
• Upgrade critical infrastructure to maintain filing season systems resiliency, leveraging cloud-
based infrastructure where practical.
11
Digital Services
Description:
Digital Services includes the self-service and online options which allow taxpayers and external
stakeholders to interact on the web via IRS websites and web applications.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Digital Services
Integrated Customer Communications Environment (ICCE), e-Services (e-SVS), IRS.GOV - Portal
Environment, Web Applications
*Under the legacy structure, ICCE, eSVS, IRS.GOV and Web Applications were categorized as Major IT Investments; some, or all their sub-investments are now
aligned under Digital Services.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
445.19
211.61
- 233.58
-
52.47%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
143.32
163.61
20.30
14.16%
Total Obligations
0.00
588.51
375.23
- 213.28
- 36.24%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of Digital Services is to revolutionize the taxpayer experience through enhancing service
offerings. The IRS plans to create a state-of-the-art digital environment for taxpayers, simplifying their
interactions with the agency. Digital Services strives to ensure services are accessible through all
channels, facilitating a seamless and enriched taxpayer experience via six projects focused on improving
digital services to taxpayers: e-Services, IRS.gov, Individual Online Account (IOLA), Business Online
Account (BOLA), TaxPro and Integrated Customer Communication Environment (ICCE). Digital
Services modernizes the way individual taxpayers interact with the IRS by providing a seamless, one-stop
digital solution to support filing, data, and communication needs. The investment transforms the way
business taxpayers interact with the IRS by providing a modern, secure, one-stop digital suite of self-
service that provides tax record information, digital correspondence, and payment capabilities to support
tax compliance. Digital Services provides a unified architecture to allow Tax Professionals to serve IRS
taxpayers across omni-digital channels and provides an improved user experience, utilizing data to drive
results and developing an intelligent enterprise where tax professionals and technology collaborate to
produce value.
The primary goals of the Digital Services investment include the realization of a comprehensive, on-
demand data view system and implementing self-service capabilities to enable business users to interact
with the IRS online efficiently and effectively, and reduce the burden of less efficient taxpayer and phone
interactions.
Through the integration of customer account, interaction, case, and compliance data, the IRS can provide
a 360-degree perspective for both IRS employees and taxpayers. Furthermore, the IRS plans to enhance
its technology to ensure equal access to information, services, and documents for all taxpayers. This will
12
be achieved through adopting multilingual standards, refactoring, and developing multilingual systems,
providing multilingual forms and notices, and integrating software-enabled translation support.
The benefits of the investment include empowering taxpayers and tax professionals with expanded digital
options for increased self-service and streamlined tax transactions. It will provide a seamless tax
experience via omni-channel, enhanced interactions for efficient customer service and increase the
availability of digital channels of contact between tax professionals and the IRS, enhancing the customer
experience. In addition, it will also improve compliance through plain language and multilingual
communications, enhance IRS.gov search, tailor outreach and simplify adherence to IRS requirements.
Additional benefits include; new IRS-hosted applications scaled to include additional value-added and
secure business taxpayer products and features that comply with the latest National Institute of Standards
and Technology (NIST).
The IRS.gov portal provides seamless one-stop web-based services to internal and external users, such as
taxpayers, business partners and IRS employees. The mission at the IRS is to provide America's taxpayers
top-quality services by helping them understand and meet their tax responsibilities, and enforce US tax
law, with integrity and fairness to all. The IRS.gov portal supports the IRS mission by providing a virtual
tax assistance center for internal and external users. In an environment of constrained resources, IRS.gov
remains a cost-efficient platform to rapidly deploy standardized customer facing solutions. During the
COVID-19 pandemic, the IRS.gov portal's ability to provide remote access to taxpayers, business
partners, and employees continued to be invaluable to the continuity of U.S. tax administration in times
when standard face to face methods increased risk to taxpayers and IRS employees. During the 2020 and
2021 filing seasons, the IRS.gov portal was instrumental in the administration of the Economic Impact
Payments to American taxpayers providing remote access to applications like Get My Payment (GMP),
the COVID-19 screening application, and Modernized Electronic filing (Mef). The IRS.gov portals
continue to support rapid application deployments that are secure and fully capable to meet taxpayer
needs. New evolving applications like Document Upload Tool (DUT) and ECM aligns the IRS with the
changing needs of taxpayers by providing them with an accessible, faster, and secure digital presence.
IRS.gov continues to improve its ability to provide better tools by supporting rapid deployment solutions,
utilizing Cloud technologies to quickly acquire secure storage, and application platforms
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• eServices deployed functionality to automate the validation of new electronic tax and information
return submitters and implemented a programmatic input channel for Income Verification
Express Service (IVES) transcript requests.
• eServices digitized the process to initiate FBI background checks to authorize electronic filers.
• Deployed “Link a CAF” to production, providing tax professionals with the ability to link their
Centralized Authorization File (CAF) number(s) to their Tax ID Number to validate authority and
enable access to expanded capabilities.
• IRS.gov Portal deployed the Document Upload Tool (DUT) and the Taxpayer Employee Facing
(TPEF) tool.
• IRS.gov Portal completed RHEL 8 upgrade in three preproduction environments: System
Integration Testing (SIT), Enterprise Integration & Test Environment (EITE), and Final
Integration Testing (FIT) environments.
• IRS.gov Portal completed the MarkLogic database build out for production.
• Completed all annual filing season prep activities for all IRS Internet portals; Public User Portal
(IRS.gov), Registered User Portal, Employee User Portal, and Transactional Processing
Environment.
13
• Released one deployment of the Business Online Account (BOLA) application, which enables
representatives of Sole Proprietorship businesses to login, gain authorization, view their business
profile, manage authorized users, and view balance due information.
• IOLA Secure Two-Way Messaging went live in Online Account in April 2023. This feature
allows taxpayers who have set up a secure messaging account through Taxpayer Digital
Communications (TDC) to securely view and reply to messages in their Online Account. This
deployment enables the IRS to reduce paper correspondence and further empowers Online
Accounts to be a “one-stop shop" for individuals to address their tax needs.
• IOLA Chat Bot – Virtual Assistant and Live Chat was deployed, allowing individual taxpayers to
interact virtually with IRS support. The Virtual Assistant is made available to eligible taxpayers
for payment-related questions which are answered through automated text interaction with the
Chat Bot. This Virtual Assistant serves as first line of defense for guided help to taxpayer
inquiries. These tools now provide handy self-service solutions for taxpayers.
• Tax Pro deployed capabilities for Link a CAF, View and Manage Authorizations, adding an
additional level of assurance, allowing tax professionals to have access to all of their active
authorizations and enabling future self-service capabilities.
• Tax Pro deployed capabilities for Individual Taxpayers: Payment Activity (Scheduled / Pending
Payment), Payment Activity (Posted Payment), and Payment Activity. (Canceled / Returned
Payment), and View Balance Due for individuals and businesses, expanding self service
capabilities so that tax professionals are able to better serve taxpayers.
• ICCE implemented OMB Audit logging for all ICCE web and telephone applications.
• ICCE expanded text chat capabilities to Online Payment Agreement (OPA) application.
• ICCE Implemented FUTURE Act – Direct Data Exchange (FA-DDX) IDR in a joint effort with
the Department of Education.
• Integrated ICCE phone applications with VoiceBot/ ACS Conversational IVR (ACI).
• Digitized fingerprint capture for efile applicant background checks.
• Deployed electronic submission of IVES individual and business transcript requests.
• Deployed electronic submission and management of Certified Acceptance Agent application.
• All Field Applications infrastructure were updated to be more current and more secure.
• Incorporated the authorization and management of all IRS Information Returns electronic filers.
• Delivered Transcript Delivery System (TDS) Application Programming Interface (API) that
delivers business transcripts through BOLA.
• Optimized transcript processing and vastly increased capacity of current infrastructure.
• .
• Updated eServices API Infrastructure to increase security and capacity.
• Incorporated a very large number of legislative changes to successfully deploy Filing Season
releases.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Incorporate Taxpayer First Act information return users within e-Services and modernize the
transcript delivery system to create a more robust web experience for the taxpayer.
• Expand Digital Service offerings across multiple service channels to meet the needs of taxpayers
and tax professionals.
• BOLA will be available to all business entity types, and will add capabilities like online business
filing, new digital communications capabilities, and account profile customizations.
• Drive IRA’s vision of transformation by delivering additional self-service options and expanding
access to Business tax professionals in BOLA programs.
14
• Expand access to Tax Pro Accounts by providing capabilities to support business tax
professionals and taxpayers.
Engagement Channels
Description:
Engagement Channels encompasses the interactions between the IRS and taxpayers or other external
stakeholders, to include; over the phone (live assistance or voice bots), via chat services (chat and live
chat), and through physical or digital notices. The Engagement Channels investment includes operating
one of the largest Contact Centers in the Federal Government, serving taxpayers though live assistance
and self-service options, meeting the taxpayer on their channel of choice. The Contact Center is one of
the most mission critical areas within IRS due to its role managing call routing for the enterprise.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Engagement Channels
Computer Assisted Publishing System (CAPS), Mail Labels and Media Support (MLMS), Notice
Conversion (NOTCON), Notice Print Processing (NPP), On Line Notice Review (OLNR),
Integrated Customer Communications Environment (ICCE), IRS Telecommunications Systems and
Support (TSS)
*Under the legacy structure, TSS was categorized as a Major IT Investment; some, or all sub-investments of TSS are now aligned under Engagement Channels and
Network.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
95.40
65.00
- 30.40
-
31.87%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
69.54
74.20
4.66
6.70%
Total Obligations
0.00
164.94
139.20
- 25.74
- 15.61%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this IT investment is to improve taxpayer engagement, utilizing advanced technology for a
seamless user experience. This investment aims to integrate voicebots and chatbots, expanding
accessibility across all available channels. With the enhancement of English/Spanish standards, system
development, and translation support, the objective is to offer equal access to information, services, and
documents for every taxpayer. The Contact Center is to deliver mission critical functionality for self-
service and assistor-based taxpayer services. Live Assistance is to enable real-time communication via a
taxpayer’s preferred channel and improve the taxpayer experience through expanded self-service and
Natural Language Processing-enabled capabilities.
The goal of this investment includes implementing industry standards and innovative technology to put
the IRS into the forefront of engagement, focusing on adaptability and inclusivity. The IRS aims to
implement advanced voice and communication tools, enabling customer service representatives to resolve
issues more swiftly. The goal is to make every interaction between taxpayers and the IRS seamless,
fostering a modern, efficient, and inclusive taxpayer experience.
15
The benefits of this investment include expanding services which ensure customer access through all
channels and modernizing the way taxpayers engage with the agency. The implementation of advanced
voice and communication tools (like Chatbot, Conversational Voice Service, Customer Call Back, and
Agent Desk Top Modernization), enables customer service representatives to resolve issues swiftly. The
integration of advanced technology will ensure a streamlined, customer-centric approach, underpinning
an exceptional taxpayer experience.
FY 2023 Accomplishments include deployment of:
• Online Account (OLA) Phase 2 Chatbot.
• The addition of Offer in Compromise Small Business/Self Employed (SBSE) New Chat Topic.
• SBSE CORR Exam chatbot.
• The deployment of the Agent Desktop Modernization (ADM) full release.
• Voice Bot Notification for System Down Time update.
• The deployment of Where's My Refund? (WMR) Voice Bot.
• The deployment of Where's My Amended Return? (WMAR) Voice Bot.
• Providing callback to additional 17 Small Business/Small Engagement (SBSE) Applications.
• Enhancements to Agent Desktop Modernization (Finesse desktop) to have Live Agents for
chatbot.
• Information Technology Service Desk (IT SD) Main Menu Natural Language Understanding
(NLU).
• 1040 Menu Conversion.
FY 2024/2025 objectives include deployment/addition of:
• W&I Customer Service Unauthenticated FAQ New Topics chat service.
• Automated under reporter (AUR) Voicebot.
• Insolvency Voicebot service.
• Specialty Collection Offers in Compromise (SCOIC) Voicebot.
• Financial Relief Conversational Voice service.
• Estate and Gift – Status of Form 706 – Authenticated Voicebot.
• Excise – Form 2290 Inquiries – Unauthenticated Voicebot.
• Electronic Performance Support Systems (PSS) e-Business Master File Automated underreported
- Voicebot: PSS Voicebot.
• Business Underreporter (BUR) – Disagree with Proposed / Actual Assessment – Unauthenticated.
• Innocent Spouse Status of Case – Authenticated Voicebot.
• Electronic Performance Support Systems (EPSS) Transmitter Codes (TCC) – Authenticated
Voicebot.
• Direct File chat request and Toll-Free Phone Line.
• Addition of Self-Service Authenticated Capabilities to the Automated Under reporter (AUR)
Chatbot.
• Government Task Manager (GTM) Integration with eGain & FDR365.
• EPSS Unauthenticated chatbot with Authenticated Live Chat.
• Innocent Spouse – Status of Case – Authenticated Chatbot and Authenticated Live Chat.
• Central Lien Operations – Unauthenticated Live Chat.
• Automated Substitute for Return (ASFR) – Authenticated Live Chat.
• Taxpayer Assistance Center Contact Modernization Phase 1.
• Taxpayer Assistance Center Contact Modernization Phase 2.
16
Filing and Intake
Description:
Filing and Intake includes the registration, ingestion, validation and perfection, error resolution, and
payment processing of all inbound electronic and paper submissions, IRS correspondence and other
inbound taxpayer information. This investment provides ingestion mechanisms for institutions to send
data for IRS and provides up-front issue detection and resolution.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Filing and Intake
Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS), Batch/Block Tracking System (BBTS), Chapter Three
Withholding Systems (CTW), Customer Service International Applications (CSIA), Electronic
Federal Payment Posting System (EFPPS), Electronic Management System (EMS), Error
Resolution System (ERS), Filing Information Returns Electronically (FIRE), Generalized Mainline
Framework/Generalized Unpostable Framework (GMF/GUF), Health Coverage Tax Credit
(HCTC), Information Returns Processing (IRP), National Account Profile (NAP) (Formerly
NAP/OLE), Remittance Processing System (RPS), Remittance Strategy for Paper Check
Conversion v2. (RSPCC), Remittance Transaction Research (RTR), Submission Processing
Measure Analysis & Reporting Tool (SMART) - A, Tax Return Data Base (TRDB), TEGE Support
Systems (TEGE SS), Modernized e-File (MeF), Information Returns Modernization (IR Mod)
formerly Business Services
*Under the legacy structure, Modernized e-file and IR Mod were categorized as Major IT Investments; their sub-investments are now aligned under Engagement
Channels.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
410.81
319.48
- 91.33
-
22.23%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
229.01
274.51
45.50
19.87%
Total Obligations
0.00
639.82
593.99
- 45.83
- 7.16%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to deploy a versatile intake platform for all tax forms and incoming
data, enhancing IRS’s adaptability to changing requirements and flexibility in customer submissions. A
modern payments platform will offer a unified account experience, accepting all government-approved
payment methods and channels.
The primary goals include achieving “digitalization at the door,” converting non-digital submissions (i.e.,
paper, fax, and image files) into machine-readable formats for efficient use and processing. Through these
improvements, the IRS aims to reduce manual processing and significantly decrease its IT footprint. This
collective effort will result in a more streamlined, user-friendly, and efficient tax processing system.
Achieving “digitalization at the door” will enable the IRS to streamline our current intake methods.
Incoming non-digital submissions (e.g., paper tax returns) will be efficiently digitalized and ready for
downstream processing. This will ultimately reduce the IT footprint by allowing us to retire legacy
systems in favor of more modernized applications.
17
The primary benefit of this investment includes the modernization of IRS intake systems which will
notably reduce taxpayer burden by promoting electronic submissions. This streamlining process will
increase efficiency and ease for taxpayers. Enhanced data integrity and integration will be achieved
through standardizing intake of tax and information returns, and digitalizing paper-based submissions,
ensuring uniform digital data for downstream processing. A significant cost reduction is another key
benefit, as the digitalization of paper-based ingestion and implementation of a modern intake platform
will significantly reduce labor-intensive manual processes and drastically decrease the IRS IT footprint.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• The expanded use of the Document Upload Tool (DUT) is now available for more high-volume
notices. This potentially can help more than 500,000 taxpayers each year who receive these
notices, which include military personnel serving in combat zones and recipients of widely-
claimed credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit and Child Tax Credit.
• Further expanded the DUT solution with the DUT for All release in September 2023, which
allows taxpayers to digitally respond to nearly all correspondence types released for digital
submission via DUT. As of December 31st, the IRS has received more than 45,000 responses to
notices via the online tool.
• As part of the Digital and Mobile Adaptive Forms (DMAF) solution, the IRS will deploy four
non-signature web-based forms using the DUT for form completion and submission in September
2023. This initial release applies to more than 380,000 annual submissions.
• Launched the Digital Enablement Platform (DEP) with scanning, extraction, and downstream
routing capabilities for initial customers in Correspondence Examination (Corr Exam) and
Automated Underreporter (AUR).
• Expanded scanning solutions for Digital Intake to Modernized e-File (DIME) for F940s, F941s,
and F1040s.
• Integrated the DUT with the DEP for automated downstream routing of applicable notices
responses (e.g., CP2000 for AUR).
• Integrated Enterprise Electronic Fax (EEFax) with Electronic File Transfer Unit (EFTU) to
automatically route faxes to the DEP for extraction and processing.
• Delivered Digitalized Content Retrieval (DCR) to provide enhanced search and reporting
capabilities of As Received.
FY 2024 Accomplishments:
• Deployed onboarding of Compliance Services Collections Operations (CSCO) to the Digital
Enablement Platform, enabling scanning, extraction, and downstream routing capabilities for the
Form 9465.
• Expanded the DUT through the release of DUT for Certifying Acceptance Agency (CAA and
multiple rounds of enhancements for DUT for Notices, enabling the digital upload of CAA
applications, supporting documents, and additional repository letters.
• Delivered 1099 Paper Processing enabling the Business to process paper Forms 1099 via the new
modernized information returns (IR) intake system as opposed to the legacy General Mainline
Framework.
• Delivered the new, modernized Information Returns Review Portal (IRRP) for paper analysts and
tax examiners to resolve errors in information returns, replacing the Error Legacy System (ERS).
• Delivered Extensions (Balance and Control) enabling downstream processing of automatic
extensions received through the IR intake system.
18
• Delivered Customer Service Representative (CSR) Partial Search Function allowing customer
service representatives to perform partial searches for information returns in the CSR portal
against various data elements.
• Delivered additional functionality in the Information Returns Intake System (IRIS) for taxpayers,
including enhanced system performance and the refactoring of existing forms to support intake
and processing time for Filing Season 24 (FS24) and multi-year submissions at the speed of 2,500
forms/second. They aim to reduce the need for future refactoring and lay the foundation to handle
future capacity needed to support broader modernization efforts (e.g., legacy system retirement,
intake of Cryptocurrency returns).
• Delivered the migration of the Information Returns Processing System (IRPS) to OpenShift
containers, accelerating technology delivery and laying the foundation for full move to cloud in
2024 and help IRS IT move forward with “Cloud First” vision and goals.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Complete Modernized e-File (MeF) schema development for 20+ prioritized forms.
• Deliver multiple extraction engines.
• Developed solution for Paper Payment Processing.
• Deliver Enterprise File Storage (EFS) and E-Fax Modernization.
• Deploy Digital Inventory Management (DIM).
• Complete Onboarding of remaining eligible DUT Notices and Letters.
• Expand onboarding of additional customers to the DEP.
• Deliver and expand Service Center Recognition/Image Processing System (SCRIPS)
modernization for incoming paper tax and information returns, ultimately scanning at point of
entry and digitally processing virtually all paper-filed tax and information returns.
• Clear 100% of Form 709s at the Independence, Missouri c-site prior to its closure in October
2026.
• Expand historical document digitalization to clear up to 1 billion priority documents at IRS
Campuses.
• Convert Historical Media Archives into stored digital formats.
• Complete installation of new Service Center Automated Mail Processing System (SCAMPS)
machines, IBML scanners, and high-end scanners to accelerate digital processing.
• Scan for digital processing up to 50% of paper-submitted correspondence, non-tax forms, and
notice responses.
• Update current transcripts to be user-friendly and available in Spanish and other languages.
• Develop mechanism to push data into return preparation software to help taxpayers prepare
current-year tax returns.
• Upgrade Online accounts to incorporate user-friendly views of account and return information
(e.g., notices, letters, account history, payment history, balances due, etc.).
• Make high-priority forms, returns, and certifications available for electronic filing and
digitalization.
• Launch payment capabilities over the phone and through IRS employees.
• Enable payments through online accounts, allowing taxpayers and third parties to make payments
through online accounts, with options to pay by bank account, credit or debit card, or digital
wallet.
• Deliver 25+ Robotic Process Automations (RPA).
• .

19
Infrastructure Management
Description:
Infrastructure Management describes IRS IT infrastructure, both in the Cloud and on-premises. This
investment includes the configurations, monitoring, and physical or Cloud-based construction of IRS IT
Infrastructure.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Infrastructure Management IRS Main Frames and Servers Services and Support (MSSS), Modernized IRS Operations
*Under the legacy structure MSSS and Modernized IRS Operations were categorized as Major IT Investments; some, or all their sub-investments are now aligned
under Storage, Compute, and Infrastructure Management.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
112.31
110.46
- 1.85
-
1.65%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
331.96
374.65
42.69
12.86%
Total Obligations
0.00
444.27
485.11
40.84
9.19%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to ensure the IRS’s IT infrastructure is robust, flexible, and adaptable to
changing needs. The focus lies in scaling and optimizing infrastructure, promoting a shift to cloud-based
solutions, and implementing managed service infrastructures on-premises. This investment aims to
automate the process of provisioning, monitoring, and managing resources, thus enhancing service
reliability, efficiency, and agility.
The primary goals of this investment include reducing operating costs and delivery timelines through
automation; standardizing infrastructure configurations for improved operational consistency;
transitioning to a scalable, cloud-based infrastructure for greater flexibility; and enhancing on-premises
infrastructure with managed services for optimized resource allocation. Achieving these goals will enable
the agency to better adapt to evolving technological requirements.
The benefit of this investment includes substantial cost savings through the reduced need for manual
resource management, improved operational efficiency due to standardized configurations, and enhanced
adaptability with the shift towards flexible, scalable cloud infrastructure. Moreover, on-premises
infrastructure will become more efficient with managed services, leading to further resource optimization.
Overall, this investment can drive a significant improvement in the IRS’s operational efficiency and
agility.

20
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Information Returns Intake System controlled launch conducted January 25, 2023, allowed
businesses to file Form 1099 series returns using a new online portal, available for free from the
IRS as required by Taxpayer First Act (TFA) legislation.
• Improved IRS employee experience by implementing M365 Mobile Device and Application
Management & migrated all Blackberry Unified Endpoint Management (UEM) users to Intune by
June 12, 2023.
• One hundred percent of on-premises mailboxes migrated to Exchange Online (EXO) & all legacy
Information Technology (IT) SharePoint sites modernized.
• Implemented Enterprise Business Intelligence Platform (EBIP) consists of Business Objects
Enterprise (BOE) and Tableau Enterprise Visualization (TEV) platforms. BOE is the IRS wide
shared services reporting infrastructure platform.
• Deployed Document Upload Tool – Taxpayer Facing Employees (DUT – TPFE) interface into
Integrated Enterprise Portal (IEP) production in December 2022, allowing taxpayers to respond to
IRS inquiries by uploading documents instead of mailing.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Continue the mission of the former MSSS investment by continuing to deliver a successful filing
season through the efficient management & maintenance of infrastructure operations.
• Leverage automation to transform operations by increasing efficiency and removing redundancies
to accelerating modernization.
• Improve the IRS infrastructure to support taxpayer facing applications as they transform to meet
customer expectations.
• Transition to cloud and managed service providers where possible.
• Perform continuous monitoring and patching of aged hardware and software assets to mitigate
security risks.
• Upgrade critical infrastructure to maintain filing season systems resiliency, leveraging cloud-
based infrastructure where practical.
Internal Operations
Description:
Internal Operations includes enterprise-wide administrative systems related to workforce support, human
capital management, accounting, financial management, procurement, facilities, and travel.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Internal Operations
Automated Labor and Employee Relations Tracking System (ALERTS), Business Performance
Management System (BPMS), Counsel Automated Legal Systems (CALS), Embedded Quality
(EQ), Employee Connection (ECON), E-Travel (IRS migration), Financial Management
Information Systems (FMIS), Integrated Planning and Information System (OPIS), OP500 Series
Programs for Returns Processing (OP500), PIV Background Investigation Process (PBIP) - B,
Reimbursable Accounts System (REACS), Redesign Revenue Accounting Control System
(RRACS), Service-wide Electronic Research Project (SERP), Totally Automated Personnel System
(TAPS)/Single Entry Time Reporting (SETR), Web Integration Collaboration and Development
(WICD), Work Request Management System (WRMS) - A, Integrated Financial System/CORE
Financial System (IFS)
*Under the legacy structure, IFS was categorized as a Major IT Investment; sub-investments of IFS are now aligned under Internal Operations.
21
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
75.91
41.91
- 34.00
-
44.79%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
217.77
247.66
29.89
13.73%
Total Obligations
0.00
293.67
289.56
- 4.11
- 1.40%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this IT investment is to help the IRS transition to more efficient and advanced operational
systems. By utilizing government-wide shared services and commercial off-the-shelf solutions, the
agency seeks to enhance its operations, improve the employee experience, and equip the workforce with
the tools they need for data-driven decision making. This investment supports critical initiatives in HR,
finance, IT service management, and eRecords management.
The goals of this IT investment include the modernization of specific systems like HR, accounting,
financial systems, IT service management platform, and an eRecords management platform. Additionally,
it aims to support the IRS’s vision of the "workforce of the future" by providing advanced collaboration
tools and an e-learning platform.
The benefits of this IT investment include empowering the IRS’s workforce with expanded self-service
options and collaboration tools that meet the modern workplace demands, fostering a knowledgeable,
diverse, flexible, and engaged team. These innovations will also enhance operational efficiency and
productivity, provides a reliable, standardized, and auditable platform for administrative accounting,
budget formulation/labor forecasting and execution (funds management) of the IRS annual budget,
contributing significantly to the agency’s resilience. By migrating platforms and systems to the cloud, the
IRS is positioned to achieve significant cost reductions, driving towards operational excellence.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Completed changes to support ongoing Federal Financial System mandates.
• Began the migration of the current IFS SAP applications to a Software Application and Products
(SAP) High Performance Analytical Appliance (HANA) Infrastructure in a Cloud Environment.
The overall migration effort will take two (2) years to complete.
• Completed the automated accrual for asset forfeiture fund.
• Completed Vendor advance payment functionality.
• Completed upgrades to components financial systems.
• Increased IT workforce enrollment in IT Academy by 168% as of May 2023 by providing IT
Academy overviews and demos during ACIO roadshows, townhalls, and IT Workforce Strategy
(ITWS) communications.
• Developed and socialized Leadership Development Current State Assessment with IT leadership
that included recommendations for evolving leadership development across IT.
• Hosted several “Journey to Leadership” Series events, to promote leadership paths and
development programs for all IT employees to drive new IRA modernization programs and
projects.
• Achieved 95 percent Knowledge Management Desk Guide completion from IT managers and
executives to meet the FY23 ACIO succession planning commitment by September 30, 2023.
22
• Exceeded ACIO Employee Engagement Commitment during second quarter by completing 183
percent of targeted chats and third quarter by completing 170 percent of targeted chats.
• Delivered legislatively mandated Inflation Reduction Act and other form changes to keep Service
Center Recognition/Image Processing System (SCRIPS) up to date.
• Transformed manual, disconnected processes that used email and spreadsheets with no visibility
into streamlined, automated, interconnected workflows.
• Coordinated workflows across Human Resource, Facilities, and IT business units, thus ensuring
all components of a request are efficiently fulfilled in a timely manner.
• Successfully expanded the legacy OS Get Services for IT Issues and requests to IRS Service
Central – the one-stop shop for IRS employees to request a wide range of services and support.
• Provided more robust functionality beyond the spreadsheet documentation previously used.
• Established a streamlined approach to resource planning.
• Bridged the IT security gap of asset alignment and reconciliation with official inventory sources
within the IRS.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Create operating model for enterprise data-analytics development and deployment spanning
research, operations, and IT.
• Develop new capacity for using aggregated and anonymized information derived from tax data to
inform policy and program decisions beyond the IRS.
• Enhance capabilities of the centralized learning platform.
• Build an accessible and multi-modal set of best-practice training programs that emphasize core
competencies and launch the platform enterprise-wide as IRS University.
• 40 percent increase in capacity to process a final investigation determination from an average of
70 per day to 100 per day by December 31, 2025.
• 20 percent increase in velocity to pre-screen an IRS employee or contractor from 70 percent of
pre-screened determinations completed within three days or less of fingerprints received to 90
percent of pre-screened determinations completed within two days or less by December 31, 2025.
• Complete the Legislative mandated interface with Treasury's G-Invoicing system for seller side
transactions.
• Complete the functionality for Clean Vehicle credit.
• Identify technical training needs to support modernization and future skills needs.
• Intentionally develop leaders and conduct succession planning to lead IT to the future.
• Enhance employee experience and inclusion through self-directed learning culture and
engagement.
• Deploy security patches, maintenance, and firmware updates.
• Deliver legislatively mandated Tax Changes to keep SCRIPS up to date.
• Continue to support and improve the digitalization SCRIPS efforts.
• Continue to support both Individual Master File (IMF) and Business Master File (BMF).
• Continue the effort to keep the SCRIPS infrastructure current.
• Consolidate existing disparate solutions and provide a path to Cloud SaaS and a more resilient
experience for employees and reduction in legacy systems footprint.
• IFS will complete the Legislative mandated interface with Treasury's G-Invoicing system for
seller side transactions.
• Complete the effort to migrate the application to the next level of SAP architecture from the
current version Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Central Component (ECC) to S/4 High
Performance Analytical Appliance (HANA).
23
• IFS will continue the effort to move to the next level of Software Application and Products (SAP)
architecture from the current version ECC to HANA on the cloud.
Network Services
Description:
Network Services includes IRS network spending, for onsite, remote, and cloud networks. This
investment describes all necessary spending to create and maintain these networks (including any
hardware or network-related software), as well as any telecommunications spending.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Network Services
IRS Telecommunications Systems and Support (TSS), Modernized IRS Operations
*Under the legacy structure, TSS and Modernized IRS Operations were categorized as Major IT Investments; some, or all their sub-investments are now aligned under
Network Services.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
113.42
126.88
13.46
11.87%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
421.94
479.96
58.02
13.75%
Total Obligations
0.00
535.35
606.83
71.48
13.35%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment includes enhancing network services for storage, computing, and users
through cloud, internet, and remote access. It is designed to modernize network infrastructure, adopting
technologies like PCI-express network fabrics and 5G, reducing IT footprint, and transitioning from wired
to mobile devices for seamless, always-connected service.
The goal of this investment includes network enhancements by embracing advanced network fabrics and
implementation of intent-based networking, designed to simplify operations, increase agility, and fortify
security through advanced automation.
The benefits of this investment include an increase to network security via geo-fencing for mobile devices
and automated network tuning for edge-content delivery. The investment also supports distributed
workflows, remote and mobile users, effectively aligning with contemporary work patterns. This leads to
a more resilient, efficient, and adaptable network system, ensuring optimal performance and user
experience.
FY 2024 Accomplishments:
• Obtained Authority to Operate (ATO) for Cloud Security Boundary - External Partner Zone.
• Performed Microsoft O365 Express Routes Upgrade from 5G to 10G.
• Completed 107 of 107 Post of Duty (POD) network bandwidth expansions.
• Completed 316 of 400 planned POD bandwidth expansions.
• Completed Engineering designs to support network expansion efforts and hybrid environments.

24
• Refreshed and decommissioned 200+ network switches.
• Refreshed voice over IP (VoIP) network attached storage infrastructure.
• Modernized provision and operation of VoIP with enhanced automation.
• Enabled Teams Direct Routing initial operating capability.
• Enabled IPv4/v6 dual stack operation across VoIP infrastructure.
FY 2025 Future Objectives:
• Transition to cloud and managed service providers where possible.
• Perform continuous monitoring and patching of aged hardware and software assets to mitigate
security risks.
• Upgrade critical infrastructure to maintain filing season systems resiliency, leveraging cloud-
based infrastructure where practical.
• Upgrade and expand network to accommodate the anticipated increase in size of the IRS
workforce and increased consumption patterns with the introduction of new digital services for
taxpayers.
• Enhance the end user experience by implementing automation, integration, and a proactive
environment.
• Upgrade and refresh VoIP Call Manager infrastructure.
• Enable IPv6-only (Internet Protocol) operation across VoIP infrastructure.
• Refresh and upgrade critical infrastructure to maintain filing season systems resiliency,
leveraging cloud-based infrastructure where practical.
Platforms & Applications
Description:
Platforms and Applications addresses the architectures, technologies, and platforms that the IRS uses to
create, deliver and deploy new enterprise applications – including API/Microservices, web and mobile
platforms, event-driven architecture, messaging and streaming middleware, application frameworks and
environments, machine learning/Artificial Intelligence, data analytics, and continuous integration /
continuous deployment tools.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Platforms & Applications
Financial Management Information Systems (FMIS), Integrated Planning and Information System
(OPIS), OP500 Series Programs for Returns Processing (OP500), PIV Background Investigation
Process (PBIP) - B, Reimbursable Accounts System (REACS), Redesign Revenue Accounting
Control System (RRACS), Service-wide Electronic Research Project (SERP), Totally Automated
Personnel System (TAPS)/Single Entry Time Reporting (SETR), Web Integration Collaboration and
Development (WICD), Work Request Management System (WRMS) - A, Integrated Financial
System/CORE Financial System (IFS)
*Under the legacy structure, SCRIPS, Web Applications, Affordable Care Act Administration, MSSS and Modernized IRS Operations were categorized as Major IT
Investments. Some, or all sub-investments are now aligned under Platforms and Applications.
25
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
86.53
72.11
- 14.42
-
16.66%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
95.38
119.72
24.33
25.51%
Total Obligations
0.00
181.92
191.83
9.92
5.45%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to ensure that the IRS possesses a cutting-edge, robust, and resilient IT
infrastructure that can deliver high-quality services and solutions. This is achieved by focusing on the
enhancement and modernization of architectures, technologies, and platforms that are utilized in the
creation, delivery, and deployment of new enterprise applications. The IRS aims to transition from aging
systems to more modern business solutions that leverage API/Microservices, Event-Driven Architecture
(EDA), enterprise web portals, and cloud-based delivery platforms. The shift towards cloud-native
applications, container platforms, and microservices aims to provide superior workload profitability and
scalability.
The goal of this investment is to reconstruct and replace outdated applications with advanced business
solutions that are future-proof and can adapt to technological changes. By employing API/Microservices,
EDA, enterprise web portals, and cloud-based delivery platforms that feature low/no-code, Platform as a
Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS), the IRS aims to expedite application delivery. Further,
the IRS is focused on the deployment of new cloud-native applications and microservices to container
platforms, thereby optimizing workload portability and scalability across on premise and cloud providers.
The benefits of this investment include accelerated application delivery due to automation in governance,
security scans, and functional testing. It ensures future-proof applications by enabling them to evolve with
changing technologies and requirements, thanks to their modular, loosely coupled components. The
adoption of container-based application deployment greatly increases the portability of applications
between on premise infrastructure and cloud platforms. Additionally, the simplification and
standardization of the agency's IT portfolio significantly reduces cost, legacy code risk, and technical debt
while improving security.
FY 2023/2024 Accomplishments:
• Enterprise Data Platform (EDP) deployed Release 2.3 on July 30, 2023, and Release 2.2 on May
30, 2023.
• Release 2.3 deployed the foundations for synchronized Individual Taxpayer Data to be available
on EDP for consumption by tenants i.e., Enterprise Case Management (ECM), Individual Master
File (IMF) Modernization (MOD) programs.
• Release 2.2 provided infrastructure capabilities for ingesting and processing data with
complicated relationships while providing the ability to deliver queries using application
programming interfaces and business intelligence tools.
• Release 2.2 provided the IRS with a world class, state of the art, and leading-edge environment
for all IRS data, which Direct Deposit Installment Agreement (DDIA), Modernized Individual
Custodial Account (MICA), soon Enterprise Case Management (ECM), and all other IRS users
and systems will be able to use for sharing data access with the appropriate security controls.
• The environment is being loaded with data from other IRS systems over the next two years and
will incrementally continue to be built out with the latest technology and data.
26
• In FY24 Q1, EDP delivered Release 2.5.2 for the Tax Account Management Services (TAMS
Release 1) on November 15, 2023. This foundational project is intended to standardize data
access for Individual Account data to support modernization efforts and will enable the
decommissioning of multiple legacy data distribution mechanisms. In addition, EDP delivered
Release 2.7 on December 10, 2023, for the Business Online Accounts (BOLA Release 2) to allow
new and existing Business Partners (General Partnerships and S-Corps) to login to BOLA and see
the businesses for which they have 1065-K1s or 1120-S forms on file.
• EDP delivered Release 3.0 on December 15, 2023, to deploy MongoDB and AppDynamics, two
technical enablers that will enable faster application development in high-performance, highly
available, and highly scalable environments.
• The Advanced Analytics Platform (AAP) will provide the IRS with a secure, scalable, and
trustworthy platform with the latest advanced analytics and Artificial Intelligence/Machine
Learning (AI/ML) technologies and techniques to provide business value to all IRS domains.
• AAP delivered its Minimum Viable Product (MVP) on August 21, 2023. AAP's MVP allows
provisioning of secure data science environments with access to data hosted in the Enterprise
Data Platform (EDP) using the Databricks infrastructure.
• The environments are provisioned with basic data science tools in either Python or R
programming languages.
• The Robotics Process Automation (RPA) creates Intelligent Automation Solutions and
implements a Unified, Enterprise-wide Automation platform with tools, technology, and process
for building, delivering, adoption and awareness of next-generation Automations.
• In Q1FY24, RPA delivered three Optical Character Recognition (OCR)/Intelligent Character
Recognition (ICR) BOTS (i.e. Robots) for the Chief Financial Officer (CFO).
• RPA developed and deployed UiPath OCR/ICR Solution for Employee Retention Credits - 941X
forms to production.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Improve IRS systems to streamline access to individual taxpayer data for service and compliance
purposes via secure, standardized APIs.
• Integrate business and IT product-and-platform operating model implemented to accelerate
technology delivery.
• Deliver data platform with advanced analytics tools for use across service, compliance, and
operations with easily consumable services.
• Make incremental improvements to the IRS API ecosystem such that we can reduce software
delivery timelines and simplify operations and maintenance through easier integration.
• Align completed evaluation of data gaps and readiness for operational use to business needs.
• Make near-real-time taxpayer service data available to IRS data scientists and analysts via
modern analytical tools.
• Give operational staff users access to self-service data analysis and report-building tools.
• Improve customer experience analytics to identify taxpayers' pain points.
• Develop advanced analytics methods to better identify tax noncompliance among high-priority
taxpayer segments, including high-income, high-wealth taxpayers and partnerships.
• Develop new analytics-enabled capabilities to support digital asset compliance.
• Formulate new methodologies to enhance and expand the estimation of tax gaps.
• Develop additional data-driven methods for enterprise-wide optimization of resource allocation
for enforcement.
• Research methods for automating or streamlining the production of high-value, customized
statistics.
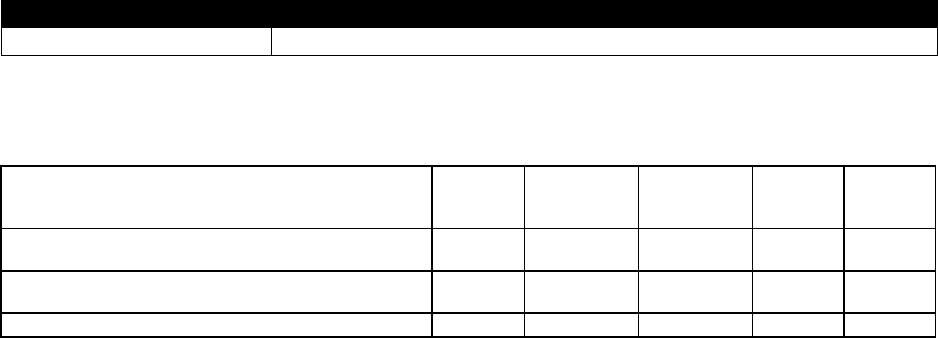
27
• Provide end-to-end visibility into application performance.
• Complete automation migration to the cloud.
• Deliver 25 automations related to Employee experience (both RPA-developed & self-service) and
Taxpayer experience.
Storage
Description:
Storage Services includes IRS spending for all systems of data storage and data encryption. Reported with
this investment is spending on cloud-based storage, physical storage resources, and archive/backup
systems for disaster recovery.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Storage IRS Main Frames and Servers Services and Support (MSSS)
*Under the legacy structure, MSSS was categorized as a Major IT Investment; sub-investments of MSSS are now aligned under Storage, Compute, and Infrastructure
Management.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
76.84
83.30
6.46
8.41%
Total Obligations
0.00
76.84
83.30
6.46
8.41%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to effectively manage the agency's data storage resources, both on
premises and cloud-based. The IRS aims to maximize storage performance and efficiency while ensuring
cost-effectiveness. This investment also focuses on transitioning from application dedicated, on premise
storage hardware to Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), shared by multiple workloads and consumers.
The goal of this investment includes the reduction of the on-premises data centers footprint and
technology capital spend. By simplifying the complexities and costs of continuous technology refreshes,
the agency aims to reduce overall IT costs and technical debt. This transformation to IaaS, combined with
managed services, will allow the agency to maintain an effective, efficient, and economically viable
storage system.
The benefit of this investment includes the reduction of costs associated with maintaining on premise
storage hardware. Further benefits include increased efficiency through the shared use of storage
resources, leading to an optimized allocation of resources. Reducing the on-premise data centers footprint
and technical debt not only cuts costs but also simplifies management processes, allowing for improved
focus on core tasks.
28
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Migrated Tier I, IRS-owned (Direct Access Storage Devices) DASD Storage to Managed
infrastructure Data Services (MIDS) eliminating maintenance for government managed storage.
• Successfully onboarded the Managed Service Provider (MSP), stood up a new Compute, Storage
Area Network (SAN) and Backup Infrastructure in each of the IRS data centers and some
campuses. Successfully migrated data and compute to the new infrastructure. MIDS had a very
successful Filing Season 2023 by delivering storage and compute with no unscheduled downtime
which allowed internal and external customers to be fully productive on all their systems.
Breakdown of activities below:
o Infrastructure Upgrades.
o Racked/Stacked new hardware for Compute, Tier 1 & 2 Storage, Backups and SAN
Switching.
o Provided new physical infrastructure for Return Review Program (RRP), Exchange, and
Modernized e-File (MeF).
o Provided Criminal Investigation (CI) new storage, compute, backup infrastructure.
o Provided new virtual infrastructure for Enterprise Information Portal/ Business Objects
Enterprise (EIP/BOE) in time for Filing Season 2023.
o Upgraded Tier 1 storage array to Gen 2 which lead led to a huge performance increase.
o Migrated virtual infrastructure off the old G9/G10 servers and retired them.
o Installed hardware and software for new backup process that allows archiving data to the
Cloud, (removing need for tapes), migrating off NetBackup (99.8% complete).
• Data Migration:
o Migrated Tier 1 data (~13PB) off of Enterprise Storage Services (ESS) storage and IRS-
owned storage.
o Migrated Tier 2 data (~35PB) off of ESS storage.
• Implemented enhanced monitoring that is integrated with Information Technology Operations
Command Center Standard (ITOCC) tools; MSP participates in Incident Management processes.
• Established ServiceNow Portal to streamline requested services from MSP.
• Coordinate all activities for unique, consumption-based contract that utilizes a Points Funding
process to provide IRS with a discount (To Date $75 million invested; approximately $30.8
million consumed).
• Developed Container as a Service (CaaS) Proof of Concept and gained approval to design, build
and moved existing container apps to the MIDS CaaS by
November 30, 2023.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Transition to cloud and managed service providers where possible.
• Perform continuous monitoring and patching of aged hardware and software assets to mitigate
security risks.
• Upgrade critical infrastructure to maintain filing season systems resiliency, leveraging cloud-
based infrastructure where practical.
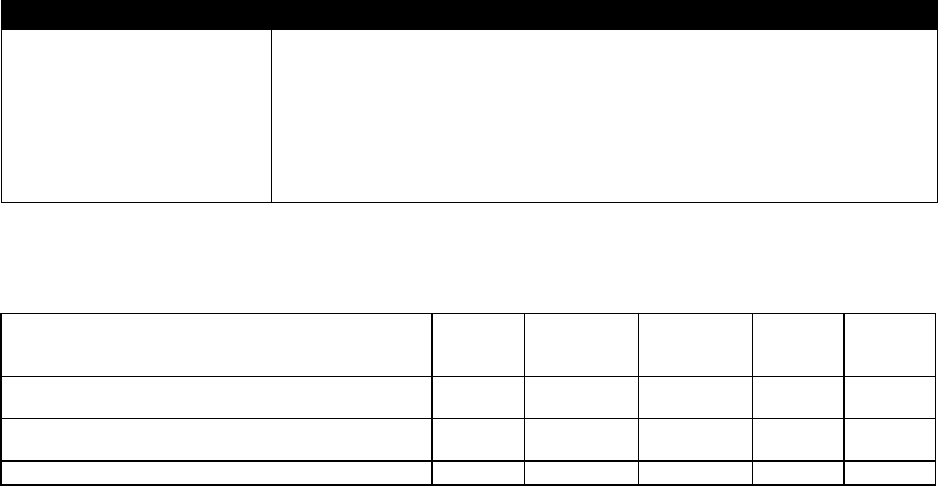
29
Tax Account Management
Description:
Tax Account Management processes all creations, updates, and deletions for a variety of tax filing
entities. Additionally, it maintains centralized access to billions of tax records and provides critical
account services to process tax returns, payments and fees, and other types of financial transactions.
Tax Account Management supports the other business areas by providing the ability to access and update
the taxpayer account data necessary to investigate, respond to, and resolve taxpayer account issues,
provide refunds for disbursement, issue notices and transcripts, etc.
Tax Account Management is responsible for tax accounting processes (e.g., financial reporting and
maintaining the general ledger) and responding to the annual Government Accountability Office (GAO)
Audit of Financial Systems.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
Tax Account Management
Name Search Facility (formerly Name Search File (NSF), Return Transaction File On-line
(RTFOL), Standard CFOL Access Protocol/Standard CFOL Overnight Processing (SCAP/SCOP),
Federal/State (FEDSTATE) (Formerly Federal/State Extract (Fed/State Extract)), Business Master
File/Individual Master File Notices (BMFIMFNOT), Notice Review Processing System (NRPS),
On Line Notice Review (OLNR), Individual Master File (IMF), Statistics of Income (SOI),
Modified EO/EP Determination System (MEDS), Compliance Tools, 701EXECRPT, Enterprise IT
Management, Individual Taxpayer Identification Number Real-time System (ITIN RTS), Tax
Return Data Base (TRDB), Individual Master File Research and Support (IMFRES), Automated
Non-Master File (ANMF), Customer Account Data Engine 2 (CADE 2)
*Under the legacy structure, IMF and CADE 2 were categorized as Major IT Investments; some, or all their sub-investments are now aligned under Tax Account
Management.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
484.78
492.08
7.30
1.51%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
99.35
170.75
71.40
71.86%
Total Obligations
0.00
584.13
662.83
78.69
13.47%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to modernize the IRS’s core tax processing systems, retire aging legacy
systems, and enhance account management capacities. By leveraging modern code, services, and
technologies, the IRS aims to cultivate a technologically advanced ecosystem that offers a more user-
centric approach to tax management. An event-driven framework and microservices / service-based
architecture will enable near real-time transaction processing, refining the IRS’s ability to manage tax
returns, fees, and account actions more effectively.
The goal of this investment includes modernization of core tax account processing to enable the
expansion of self-service options for individuals and businesses through enhanced transaction processing
and easier access to data with the integration of the Enterprise Data Platform (EDP) and deploying
30
modern data access services. The IRS aims to transform its notice and correspondence processing
environment, making it more streamlined to generate, review, distribute, and archive notices. Overall, the
goal is to deliver a modern, efficient, and user-friendly tax processing environment.
The benefit of this investment includes the modernization of the IRS’s core tax processing systems which
is fundamentally an operational risk mitigation to move away from reliance outdated programming
languages and restrictive data structures that are no longer taught and increasingly no longer known
except for a subset of people who grew up using it and are retirement eligible.
The following high-level outcomes are expected through this investment:
• Reduce Operational Risk / Resiliency / Simplification - Core account data, processing, and case
management systems are straightforward to update and maintain with common technical skills
(e.g., engineering and development) available in the market today (assuming training in tax
administration).
• User Experience / Data Access - Authorized taxpayers, employees, and systems can access core
account and case data in near real time with appropriate security controls and monitoring to
prevent unauthorized access.
• Velocity / Flexibility - IRS can implement new or expanded capabilities, legislative mandates,
and tax code changes faster, more frequently, and more incrementally.
• Enhanced flexibility, modularity, and availability are key to enabling a smoother, more efficient
tax processing experience. Furthermore, accurate and timely data significantly improves issue
resolution speed and financial reporting precision, enabling the IRS to serve the taxpayer better.
Near real-time processing leads to improved compliance during filing, agility, and responsiveness
in end-to-end tax processing. Overall, this investment will bolster tax processing, allowing for a
more streamlined and taxpayer centric approach.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Individual Tax Processing Engine (ITPE) Project completed High Volume Function Testing on
modernized Java Run 12 and Run 15 Filing Season 22 (FS22) code base.
• Deployed Taxpayer Information Service and initial APIs as part of the Taxpayer Account
Management Services (TAMS) Project - Release 1 which provides access to Individual Taxpayer
data.
• Performed analysis of IMF 701 load modules (reports / extracts) and documented findings based
on data needs, solution patterns, and end-users / customers in order to begin modernization or
retirement of all IMF 701 components.
• Developed target state conceptual architecture for Tax Account Management- Individual (TAMI)
in alignment with Enterprise Holistic architecture to include Event Driven Framework and micro-
services.
• IMF continues to fill the functional needs of the individual taxpayer account processing and to
perform Operations and Maintenance for tax law changes.
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Initiate implementation of real-time data processing to provide timely transactions (refunds,
notifications, etc.) and meet taxpayer expectations.
• Establish data distribution services to streamline access to taxpayer accounts.
• Modernize core tax processing systems and reporting tools to enable better insight into operations
and real-time financial reporting.

31
• Provide ability to access and update taxpayer account data necessary for other key business
functions across the enterprise.
• Begin updating the programming languages in legacy master files, rewriting these systems in
modern development languages.
• Translating key IMF runs from Assembly Language Coding to Java in conjunction with the
CADE 2 and Individual Tax Processing Engine projects.
• Interact with programs that impact IMF.
• Continue performing Operations and Maintenance for tax law and maintenance changes.
• Establish Modern Business Tax Account Database on the EDP.
• Services to Enable Prioritized Business Online Account (BOLA) Functionality
• Modernize BMF Data Validation Service.
• Deliver Initial Self-Service Reporting Tool with High Priority Reports.
• Modernize and refactor the Employee Plans Master File.
User Services
Description:
The IRS employee experience will include any IRS Government-Furnished Equipment (GFE) and shared
tools for collaboration, communication, or productivity, as well as input-output services such as printing
and scanning supporting day-to-day operations.
Consolidation of previous investments:
Major Investment
Sub-investments
User Services IRS End User Systems and Services (EUSS)
*Under the legacy structure, EUSS was categorized as a Major IT Investment; sub-investments of EUSS are now aligned under User Services.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
72.64
1.16
- 71.48
-
98.40%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
504.29
588.67
84.38
16.73%
Total Obligations
0.00
576.93
589.83
12.90
2.24%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The purpose of this investment is to provide secure, reliable, innovative, and cost-effective IT computer
hardware, software, services, and support for IRS employees in delivering the IRS's Tax Administration
mission. User Services provides end user focused Information Technology (IT) products and services for
all IRS employees. User Services includes annual funding for the provisioning of end user technology as
well as the day-to-day operations, maintenance, services, and support of all end user technologies at the
IRS as required by Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act (FITARA).
32
The goal of User Services includes maintaining a secure, stable, and innovative workplace computing
environment that provides IRS employees with state-of-the-industry computing devices, applications,
security defenses, business tools and associated end user services to maximize their uptime and
productivity, while providing compliance with both NIST and Defense Information Systems Agency
(DISA) security requirements. Additionally, the User Services facilitates delivery of user focused IT
projects and initiatives that enable communication, collaboration, and business capabilities in alignment
with the IRS's Integrated Modernization Plan and the IRS Strategic Plan.
The benefit of this investment includes the enhancement of end-user experience and operational
efficiency. Equipping the IRS workforce with physical devices such as laptops and leveraging a Virtual
Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) through mobile devices and thin-client equipment, such as laptops and VDI,
increases flexibility and productivity. A robust infrastructure can cater to varying workload demands,
improving employee satisfaction and service quality. Simultaneously, advanced input-output capabilities
enable seamless media transition, ensuring efficient ingestion or output of both digital and physical
content. This reduces the time taken to process data and streamlines operations such as scanning, printing,
and recording, yielding time and cost efficiencies.
FY 2023 Accomplishments:
• Replaced 21,804 laptops and processed 39,000+ disposals.
• Deployed 19,345 new hire workstations and 3,964+ hoteling stations.
• Created 494 software deployment packages, equal to 6.6 million individual deployments to
workstations with a 95 percent success rate.
• Achieved an overall Tier 3 aged software currency goal of 11.5 percent.
• Deployed 10,000+ monitors to Return to Office operations.
• 86 software applications were completed as of August 2023, with 10 more in the pipeline.
• Completed evaluating an additional 100 software applications for FY24.
• Removed 24 client software assets from the software portfolio.
• Removed about 22 thousand inactive workstations in Active Directory.
• Operationalized all SPLUNK IT Asset Management (ITAM) Applications providing clear
visibility in IRS full IT Portfolio of hardware, software, virtual, cloud and managed assets.
SPLUNK is a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) software solution tool.
• Deployed pre-authenticated voice Bot for IT Service Desk that captures employee ID and
populates screen with employee information for specialist. This provides a better employee
experience by avoiding an employee having to repeat the information such as Name, POD, Phone
number etc. to specialist.
• Deployed integration of eGain Live Chat enabling auto switch between phone and chat to meet IT
Service Desk demands.
FY 2024 Accomplishments
• Replaced 11,419 laptops and processed 12,834+ enterprise-wide disposals, including over 5,100
computer disposals.
• Deployed over 11,076 new hire workstations and over 870 hoteling stations, Year To Date
(YTD).
• Achieved an overall Tier 3 aged software currency goal of 17 percent.
• Successfully awarded Info Connect Micro Focus contract with a base year and 3 option years.
33
FY 2024/2025 Future Objectives:
• Migrate ITMS Automated Software Deployment tool to version 8.7 on Windows Server 2019
platform.
• Migrate all IRS COE clients from Window 10 to Windows 11.
• Modernizing Common Operating Environment (COE) Application Registration (App Reg)
database; leading agile, scrum approach; standups, demos, sprints with Microsoft to migrate
critical App Reg database to Teams or SharePoint.
• Transition to ServiceNow Information Technology Asset Management System Out of the Box
capabilities. MSP has re-baselined project timeline from June 2024 to a new go-live of November
2024.
• In support of the Increase in Presence Return to Office directive from the DoT, we are providing
IT equipment and personnel, to deploy shared workstations.
• Implementing additional Rapid Equipment Deployment and Disposal (REDD) sites at
Philadelphia, Chamblee, and Jacksonville (resource dependent) to streamline support to the local
IT community and to enhance customer support and satisfaction.
• Expansion of IT Service Desk interface for fully automated interactions and responses to provide
technical support for Bot technologies, exploring Separating Employee Clearance (SEC) and
Laptop Combo Lock resets.
• Automate leave collection capabilities for IT Service Desk, currently reviewing 3 options by the
vendor.
• Exploring Automated Embedded Quality Review System (EQRS) and assessing options
including quality review, agent prompting and customer sentiment capabilities
• Skill Based Routing completed. Phase 2 of the project is inflight, centering around training
improve phone resource skill proficiency levels.
• Deploy/Replace scanning devices to Business Customers for IRA Digitalization
• Expand Symantec Self-Service portal to add all unrestricted/unlicensed products and create a
Business Entitlement Access Request System (BEARS) entitlement approval process for all
restricted and licensed software.
• Develop proof of concept for Windows Autopilot to transition to a Zero Touch Workstation
Deployment Model.
• Transition to ServiceNow Information Technology Asset Management System Out of the Box
capabilities.
• Develop a Microsoft Power Business Intelligence (BI) connector to Common Operating
Environment Application Registration database to provide a real-time software pipeline process
dashboard on SharePoint.
• Automate leave collection capabilities for IT Service Desk.
• Implement Scheduled Call Back feature for employees calling the IT Service Desk, to setup time
for call back so a tech can fix issues, reducing hold times.
• Adapt Robotics Process Automation (RPA) technology to design, build, implement, and maintain
RPA solutions for the automation of Customer Service Sections use cases and implementation of
business and technical requirements with the IRS ServiceNow environments.
• Expansion of IT Service Desk interface for fully automated interactions and responses to provide
technical support for Bot technologies.
• Streamline the process to a single vendor to provide end user laptop and desktop computing
devices in an innovative and efficient manner.
• Develop and deploy the Virtual Desktop Infrastructure to support initial use cases of
Supplemental Workstations and Contractor as well as potential future use cases.

34
Major Non-IT Investments
Criminal Investigation Owned Vehicles
Description:
The IRS-Criminal Investigation Business Unit maintains ownership of approximately 74 Vehicles to
include Commissioners Protective Detail and surveillance type vehicles. Excluded are Criminal
Investigation Under Cover and International Vehicles that are not reported in Treasury's FAST System
due to sensitivity.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
2.50
2.50
3.20
0.70
28.00%
Total Obligations
2.50
2.50
3.20
0.70
28.00%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The IRS-Criminal Investigation Business Unit vehicles are used for surveillance, for the Commissioner's
protective detail and to support the IRS investigations and must meet the mission critical need to conduct
criminal law enforcement activities.
Leasehold Improvements
Description:
Leasehold Improvements managed in AWSS.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
7.97
24.85
16.88
211.79%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
103.84
193.88
162.94
-
30.94
-
15.96%
Total Obligations
103.84
201.85
187.79
- 14.06
- 6.96%
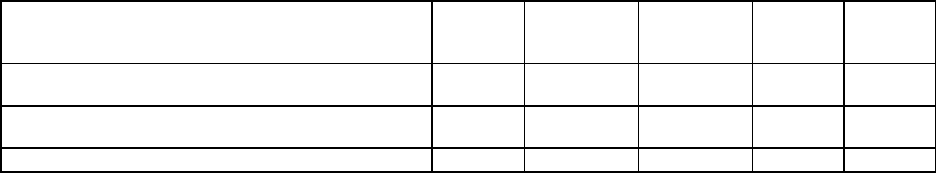
35
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
Many projects undertaken by IRS entail the design, alteration, and furnishing of space either upon
acquisition, at lease renewal, or for other purposes, such as supporting space consolidation or reduction.
The portion of the project that is captured as a capital asset is reflected in OMB Object Class 3200, Land
and Structures, and includes alterations to buildings; fixtures such as elevators, plumbing, power-plant
boilers, fire-alarm systems, lighting, heating systems, air-conditioning systems, flooring, and carpeting.
The total figure is a sum of the expenditures in that object class for all IRS projects in that particular year.
Security Equipment
Description:
Security Equipment is managed in FMSS.
Investment Obligations: (In Millions of $):
Type
FY 2023
Actuals
FY 2024
Estimated
Obligations
FY 2025
Estimated
Obligations
Change
in $
%
Change
Sub- Total DME Obligations (Including Internal
labor (Govt. FTE))
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00
0.00%
Sub- Total O&M Obligations (Including Internal
Labor (Govt. FTE))
3.84
3.20
3.20
0.00
0.00%
Total Obligations
3.84
3.20
3.20
0.00
0.00%
Purpose, Accomplishments, Future Objectives:
The IRS purchases security equipment such as cameras, digital video recorder system (DVRs), access
control panels, and card readers. The IRS uses facility-specific security assessments to prioritize asset
needs and develop criteria for replacing equipment in a given facility. Additionally, emergency needs
arise over the course of the year. These needs are ranked and funded according to the effect the
equipment has on the overall security posture.
The need for equipment can arise at any time, such as when employees are moved into a new building,
during internal moves, or intermittently when equipment needs to be replaced. The benefit of this capital
asset investment is that it supports the IRS priority to provide a safe and secure environment for its
employees, equipment, and facilities.
36
Appendix 1: Legacy Investment Crosswalk to
New IT Investment Structure
Legacy Investment Crosswalk to New IT Investment Structure
Major IT Investments - LEGACY*
FY 2023
Actuals
New IT Investment Structure
Account Management Services (AMS)
12.482
Case Management
Affordable Care Act Administration (ACA)
70.875
Platforms & Applications
Authorization Authentication Access e-A3
86.831
N/A
Business Master File (BMF)
62.692
Compliance, Tax Account Management
Compliance Tools
10.392
Case Management, Compliance, Tax Account Management
Customer Account Data Engine (CADE 2)
219.939
Tax Account Management
Cybersecurity Ops, Risk Mgmt and Imp
409.242
N/A
Enterprise Case Management (ECM)
119.432
Case Management
e-Services (e-SVS)
12.380
Digital Services
Foreign Acct Tax Compliance Act (FATCA)
23.202
N/A
Individual Master File (IMF)
84.597
Tax Account Management
Int Cust Comm Environment (ICCE)
12.164
Digital Services, Engagement Channels
Int Subm and Remittance Proc Sys (ISRP)
7.702
N/A
Integrated Data Retrieval System (IDRS)
16.201
Case Management
Integrated Fin Sys/CORE Fin Sys (IFS)
26.002
Internal Operations, Platforms & Applications
IR Modernization
78.093
N/A
IRS End User Systems and Support (EUSS)
341.953
User Services
IRS Telecommunications Sys Supp (TSS)
464.886
Engagement Channels, Network Services
IRS.Gov - Portal Environment
84.705
Digital Services
Main Frames & Servers Serv Supp (MSSS)
781.151
Compute, Infrastructure Management, Platforms &
Applications, Storage
Modernized e-File (MeF)
58.655
Filing and Intake
Modernized IRS Operations
202.991
Infrastructure Management, Network Services
Return Review Program (RRP)
49.498
Compliance
Svc Ctr Recogn Imaging Proc Sys (SCRIPS)
8.071
Platforms & Applications
Web Applications
135.569
Digital Services, Platforms & Applications
Total Major IT Investments - LEGACY
3379.704
Total Non-Major IT Investments - LEGACY
726.594
*Under the legacy structure these investments were categorized as Major IT Investments; in most cases, some, or all of the sub-investments under the legacy
major investments were realigned under the new Major IT investment structure.
