
DEPARTMENT OF THE AIR FORCE CFETP1A1XX
Headquarters US Air Force Part I-II
Washington, DC 20330-1030 30 July 2024
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR
1A1XX
CAREER FIELD
EDUCATION AND TRAINING PLAN
(CFETP)
ACCESSIBILITY: Publication and forms are available on the e-publishing website at www.e-publishing.af.mil for
downloading or ordering.
RELEASABILITY: There are no releasability restrictions on this publication.
CFETP 1A1XX
2
Table of Contents
PART I
Preface ............................................................................................................................................................................................................ 4
ABBREVIATIONS/TERMS EXPLAINED ............................................................................................................ 5
SECTION A – General Information ...................................................................................................................... 10
SECTION B – Career Progression and Information ............................................................................................... 11
Specialty Descriptions ....................................................................................................................................... 11
1A1X2 Mobility Force Aviator .......................................................................................................................... 11
1A1X3 Special Mission Aviator ......................................................................................................................... 11
1A1X4 Multi-domain Operations Aviator .......................................................................................................... 11
1A1X8 Executive Mission Aviator .................................................................................................................... 12
Training Decisions ............................................................................................................................................. 12
Community College of the Air Force (CCAF) Academic Programs.................................................................... 12
Career Field Flow Charts ................................................................................................................................... 13
SECTION C – Skill Level Training Requirements ................................................................................................. 15
Purpose .............................................................................................................................................................. 15
Specialty Qualifications ..................................................................................................................................... 15
Apprentice (3) Level .......................................................................................................................................... 15
Journeyman (5) Level ........................................................................................................................................ 15
Craftsman (7) Level ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Superintendent (9) Level .................................................................................................................................... 16
SECTION D – Resource Constraints ..................................................................................................................... 17
Purpose ............................................................................................................................................................ 17
Apprentice Level Training ................................................................................................................................ 17
Journeyman Level Training .............................................................................................................................. 17
Craftsman Level Training ................................................................................................................................ 17
PART II
SECTION A – Specialty Training Standards (STS) ................................................................................................ 18
SECTION B – Course Objective List ..................................................................................................................... 18
SECTION C – Support Material ............................................................................................................................ 19
SECTION D – Training Course Index ................................................................................................................... 19
SECTION E – MAJCOM Unique Requirements ................................................................................................... 25
SECTION F – MAJCOM Unique Resource Requirements .................................................................................... 25
Attachment 1 Qualitative Requirements ................................................................................................................. 26
Attachment 2 Career Enlisted Aviator Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References ............................................. 27
Attachment 3 Mobility Force Aviator Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References ............................................. 31
Attachment 4 Special Mission Aviator Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References ............................................ 32
Attachment 5 Multi-domain Operations Aviator Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References .............................. 34
Attachment 6 Executive Mission Aviator Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References ........................................ 36
OPR: HQ USAF/A3TS
Certified by: HQ USAF/A3TS (CMSgt Gregory Gibbs)
Supersedes: CFETPs 1A1XX (24 May 2023), 1A3X1 (18 September 2018), 1U0X1 (29 Mar 2021)
Total Number of Printed Pages: 39
CFETP 1A1XX
3
List of Figures and Tables
Figure 1. CEA Career Path ................................................................................................................................ 39
Table 1. Enlisted Education and Training Path ................................................................................................ 14
Table 2. MFA Air Force In-Residence Courses ................................................................................................ 19
Table 3. AMC Distance Learning Courses ........................................................................................................ 20
Table 4. MFA Advanced Training ..................................................................................................................... 20
Table 5. EMA Air Force In-Residence Training ............................................................................................... 21
Table 6. EMA Contracted Training ................................................................................................................... 21
Table 7. SMA Air Force In-Residence Courses ................................................................................................ 21
Table 8. MOA Air Force In-Residence Courses ............................................................................................... 23
Table 9. Air Education and Training Command Courses ............................................................................... 24
Table 10. Career Enlisted Aviator Advanced Training.................................................................................... 24
Table 11. ANG Mission Essential Skills Training Days .................................................................................... 25
CFETP 1A1XX
4
CAREER FIELD EDUCATION AND TRAINING
PLAN CAREER ENLISTED AVIATORS
AFSC CEA
PART I
Preface
1.
This Career Field Education and Training Plan is a comprehensive education and training document that identifies life-
cycle education/training requirements, training support resources and minimum core task requirements for this specialty.
The CFETP provides personnel a clear career path to success and instills rigor in all aspects of career field training. At
unit level, supervisors and instructors use Part II to identify, plan, and conduct training commensurate with the overall
goals of this plan.
2.
The CFETP consists of two parts and six attachments:
2.1.
Part I provides information necessary for the overall management of the CEA career field and is divided into
four sections. Section A - General Information; Section B - Career Progression Information; Section C - Skill Level
Training Requirements; Section D – Resource Constraints; some examples are funds, workforce equipment, and
facilities. Note: The Air Force Enlisted Classification Directory (AFECD) and AFMAN 36-2100 Military Utilization
and Classification contain the specialty descriptions.
2.2.
Part II includes information regarding training requirements and is divided into six sections. Section A-
identifies the Specialty Training Standard (STS) and includes duties, tasks, technical references to support training,
AETC conducted training, and correspondence course requirements. Section B- contains the course objective list
and training standards supervisors will use to determine if Airmen satisfy training requirements. Section C
identifies available training support materials. Section D- identifies a training course index that is used to determine
resources available to support training. Included here are both mandatory and optional courses. Sections E and F
identify MAJCOM unique training resource requirements. Attachment 1 of the CFETP defines the qualitative
requirements for successful completion of Undergraduate Flying Training. Attachments 2 through 6 list all
training line items required for CEAs to be awarded a 3-skill level.
2.3.
Figure 1 provides a visual depiction of the CEA career field path. This chart provides a timeline for
achieving additional qualifications such as instructor, evaluator, and Formal Training Unit (FTU)
assignment. Lastly, the chart identifies leadership opportunities within the squadron, group, wing,
MAJCOM, and HQ/USAF.
CFETP 1A1XX
5
ABBREVIATIONS/TERMS EXPLAINED
Note: The abbreviations and terms below have been identified as commonly used within all Career Enlisted Aviator
specialties.
Advanced Instructor Course (AIC). A formal instructor course to provide advanced academic, simulator, and
flight training with a focus on building and developing tactical, technical, and instructional expertise. The overall
vision is to generate elite tacticians to develop instructional methodology, codify technical expertise, and establish
instructional continuity within the specialty.
Air Force Career Field Manager (AFCFM). Representative appointed by the respective HQ USAF Deputy Chief
of Staff or Under Secretariat, to ensure assigned AF specialties are trained and utilized to support AF mission
requirements.
Air Force Force Generation (AFFORGEN). A 24-month cycle composed of four, six-month readiness phases that
ensure a sustainable force offering of Airmen and airpower to the Joint Force. The four AFFORGEN phases align
with the Joint Staff’s three phase model. AFFORGEN phases are: Available to Commit, Reset, Prepare, and Certify.
Air Force Form 8/8A (AF Form 8/8A) Certificate of Aircrew Qualification. The source document to record the
aircrew evaluation and verify the qualification of an aircrew member. The AF Form 8/8A is used to record aircrew
maintaining qualification in a single aircraft. The AF Form 8/8A is used to record aircrew maintaining universal or
multiple qualifications IAW 11-202V2, Aircrew Standardization and Evaluation Program.
Air Force Specialty Code (AFSC). An alphanumeric combination used to identify an Air Force Specialty (AFS).
Officer AFSCs consists of four characters and/or digits. Airmen AFSCs consist of five characters and/or digits.
When more specific identification of position requirements and individual qualifications is needed, alpha prefixes
and suffixes are used with the numerical codes.
Air Reserve Component (ARC). Air National Guard and Air Force Reserve units.
Aircrew Graduate Evaluation Program (AGEP). A survey completed by FTU graduates and conducted in
accordance with AETCI 36-2621, Flying Training Course Publications Development. Feedback gathered through
the AGEP is used to ensure AETC formal flying training course graduates meet customer requirements. The AGEP
goal is to provide training program managers and senior leaders a comprehensive assessment of training
effectiveness and areas of improvement.
Aircrew Training System (ATS). A system wherein a civilian contractor provides academic, simulator and other
designated aircrew training methods. ATS courses are listed in the applicable AFMAN 11-2 MDS-Specific,
Volume 1 or the Education and Training Course Announcement (ETCA) website (https://etca.randolph.af.mil).
Airman Leadership School (ALS). ALS is a resident Community College Air Force (CCAF)-affiliated program
that consists of 192 curriculum hours. The curriculum prepares Senior Airmen and Guardians to be professional,
war-fighting Airmen and Space Professionals who can supervise and lead work teams as an all-domain joint
warfighting professional to support the employment of an Air and Space power.
Basic Aircraft Qualification (BAQ). Applies to an aircrew member who has satisfactorily completed IQT and is
qualified to perform aircrew duties in the unit aircraft. The member must perform at the minimum frequency
necessary to meet the most recent sortie and flight standards set for that weapon system in the applicable AFMAN
112MDS Volume 1.
Basic Military Training (BMT). Training provided to non-prior service (NPS) Airmen to affect an orderly
transition from civilian to military life.
Basic Mission Capable (BMC). An aircrew member who has satisfactorily completed IQT and MQT, is qualified in
some aspect of the unit mission, but does not maintain MR/CMR status. The aircrew member must be able to attain
full qualification to meet operational taskings within 30 days, or in accordance with the applicable AFMAN 11-
2MDS Volume 1.
Career Enlisted Aviator (CEA). An enlisted aircrew member that is highly trained to conduct various roles and
capabilities in support of USAF and joint multi-domain mission sets. A CEA maintains requirements to possess any
of the 1A1XX specialties.
Career Enlisted Aviator Center of Excellence (CoE). Located at Joint Base San Antonio-Lackland, TX and
CFETP 1A1XX
6
provides aircrew candidates basic aviation skills and training to prepare Airmen for IQT at formal training units.
Career Enlisted Aviator Fundamentals Course (CEAFC). An enlisted undergraduate flying training course
which prepares enlisted personnel for a career in aviation. The knowledge presented in the course includes
physiological, survival, aircrew mission, anti-hijacking and anti-terrorism, aircrew coordination, aircrew training,
basic aerodynamics, aircraft publications, safety, and flight medicine. This course screens for the ability to handle
the rigor of aircrew duties prior to entering costly follow-on training.
Career Enlisted Aviator Senior Leader Course (CEASLC). A course that proactively prepares TSgt and MSgt
CEAs for future roles as Operations Superintendents and Squadron SELs. This course focuses on transitioning
NCOs and SNCOs into operational leaders with an understanding of strategic aircrew management. CEASLC covers
the unique attributes of effectively managing CEAs and prepares airmen for operational leadership roles at, and
above, the squadron level. Course content is presented in a guided group discussion format for all 1A/1U AFSCs on
Operational and Strategic Competencies, Strategic Structure, Force Management and Career Field Mapping.
Career Enlisted Aviator Staff Course (CEASC). A course that prepares SNCOs selected for duties in Key
Development and Key Leadership Positions at the NAF, MAJCOM, AFPC, or HAF. Course material is focused on
strategic level aircrew management programming and executive level communication.
Career Field Education and Training Plan (CFETP). A CFETP is a comprehensive core training document that
identifies life-cycle education and training requirements. It also provides training support resources and minimum
core task requirements for a specialty, aims to provide personnel a clear career path and instill a sense of industry in
career field training.
Chief Master Sergeant Leadership Course (CLC). CLC, located on Maxwell-Gunter AFB, AL, is a resident
program that consists of 80 classroom hours. The CLC is designed to prepare Chiefs for their initial CMSgt roles
and responsibilities, primarily targeting Chiefs serving at the squadron level. This course provides Chief Master
Sergeants the education to bridge strategic vision into tactical execution. Throughout the program, the CLC
emphasizes critical thinking and an enterprise-level view in order to educate, inspire, and develop Chief Master
Sergeants who effectively lead, manage, and mentor lethal and ready organizations. Chiefs will attend the CLC
within two years of receiving their promotion line number. Chiefs will continue to build on foundational leadership
competencies invaluable to fly, fight, and win across the full-spectrum of conflict and all domains of military power.
Combat Mission Ready (CMR). An aircrew member who has satisfactorily completed IQT, MQT, and maintains
qualification and proficiency in the command or unit combat mission.
Community College of the Air Force (CCAF) Academic Programs. Airmen are automatically enrolled in CCAF
upon completion of basic military training. CCAF provides the opportunity to obtain an Associate in Applied
Science (AAS) Degree.
Continuation Training (CT). The continuation training program provides crew members with the volume,
frequency, and mix of training necessary to maintain proficiency in the assigned certification/qualification level.
Core Task. A task identified by the AFCFM as a minimum qualification requirement within an AFS or duty
position. Core Tasks for the AFS can be either task or knowledge-based and are the STS line items fundamental to
meeting these core competencies. Each MAJCOM is responsible for developing the minimum standard to which
each core task will be trained. Core skills (or knowledge) must be trained, maintained, and certified, regardless of
duty position/location and are based upon skill level.
Course Objective Lists (COL). A publication derived from the initial and advanced skills course training standard
(CTS), identifying the tasks and knowledge requirements, and respective standards provided to achieve a 3-, 5-, or
7- skill level in this career field. Supervisors use the COL to assist in conducting graduate evaluations.
Course Training Standard (CTS). A training standard identifying the training members will receive in a specific
course.
Crew Resource Management (CRM). The effective use of all available resources—people, weapon systems,
facilities and equipment, and the environment by individuals or crews to accomplish an assigned mission or task
safely and efficiently. The term “CRM” will be used to refer to the training program, objectives, and key skills
directed to this end.
Enlisted Joint Professional Military Education I (EJPME I). This certificate course is designed to help educate
CFETP 1A1XX
7
and prepare enlisted leaders assigned to joint organizations or those going to joint assignments. Upon completion of
the course, students will be better prepared to: operate or work in a joint environment or organization; lead
members of multiple Services; and contribute to joint mission success.
Enlisted Joint Professional Military Education II (EJPME II). This certificate course is designed to build upon
the material presented in the EJPME I course. This certificate course is designed to educate and prepare enlisted
leaders assigned to joint organizations to successfully support activities; lead members of multiple Services; and
better understand operating in a joint environment.
Enlisted Undergraduate Flying Training (E-UFT). A formal school course that results in the award of a 3-skill
level AFSC. CEA Initial Skills Training consists of Undergraduate Flying Training (CEAFC and SERE), Graduate
Flying Training (also referred to as IQT) in a specific MDS aircraft and an AF Form 8/8A, Certificate of Aircrew
Qualification to earn the award of a 3-skill level AFSC.
Evaluator Aircrew member. A highly qualified and experienced instructor qualified in a particular crew position
that is selected and designated in writing by the SQ/CC or OG/CC to administer flight evaluations to CEAs in that
crew position.
Exportable Training (ET). Additional training via computer, paper, interactive video, or other necessary means to
supplement training.
Formal Training Unit (FTU). A unit whose principal mission is to conduct IQT in accordance with a MAJCOM
certified syllabus that result in a crew position qualification in a MDS aircraft.
Initial Qualification Training (IQT). Graduate Flying Training required to qualify aircrew for basic aircrew duties
in an assigned crew position for a specific aircraft, without regard for the unit’s operational mission (Example: C-
130J Loadmaster). IQT also occurs during the upgrade training process (Example: Instructor upgrade qualification).
It is designed to provide the performance skill/knowledge training required to perform a MDS mission or act in a
higher qualification.
Instructional System Development (ISD). A deliberate, orderly, but flexible process for planning, developing,
validating, implementing, and reviewing instructional programs. Ensures personnel are provided the skills necessary
for successful job performance, with fiscal responsibility in mind.
Instructor Aircrew (IXX). A crewmember trained and authorized to instruct other CEAs in crew position(s) for
which they are certified/qualified.
Junior Enlisted Foundations Course 300 (JEFC300). JEFC300 bridges the gap between tech school and Airman
Leadership School. The course provides students with the foundational skills and knowledge needed to conform to
standards, customs and courtesies, and offers guidance to help enhance the students’ focus on becoming highly
efficient career field and 5-skill level agents. The JEFC300 empowers Airman to reflect on their behaviors in
relation to the Airmen Leadership Qualities. It facilitates the journey to developing supervisory and leadership skills,
developing the competency of leading individuals and teams, and understanding the guardrails and guidelines of
supervision.
Lead Command. A MAJCOM is responsible for an assigned weapons system. Lead Commands establish advocacy
for designated weapon systems during their life cycle and clarify responsibilities for all using and supporting
organizations. They provide primary input into the purpose of developing and maintaining a force structure with a
balance of complementary capabilities.
Major Command (MAJCOM) Functional Manager (MFM). Primary focal point and liaison between the
MAJCOM/NAF/DRU and HQ USAF on all matters relating to the aircrew career fields and aviation resource
management within the command. This includes, but is not limited to, responsibility for the aircrew training
programs, coordination on aircrew resource allocations, and managing education, training, and resources for a
specific career field(s) for their organization. A Functional Manager’s scope may include all CEAs within a
MAJCOM/NAF/DRU, MWS, or MDS.
Major Weapons Systems (MWS). Several like Mission Design Series (MDS) comprise a Major Weapons System
(MWS) category (e.g., the bomber MWS is comprised of the B-1, B-2, and B-52 MDSs).
Mission Design Series (MDS). A term used to identify a specific aircraft designation. (Example: UH-1N)
CFETP 1A1XX
8
Mission Qualification Training (MQT). Training required to qualify crewmembers in an assigned crew position
for a specific MDS to perform the command or unit mission. MQT often results in a CMR or MR
certification/status. CEAs are awarded a 5-skill level upon completion of MQT.
Mission Ready (MR). An aircrew member who has satisfactorily completed IQT, MQT, and maintains qualification
and proficiency in the command or unit operational mission.
Noncommissioned Officer Academy (NCOA). The NCOA course is a resident Community College of the Air
Force (CCAF) affiliated course that consists of 196 hours of classroom instruction delivered over 25 academic days.
The overall goals of NCOA are to develop the leadership capability of NCOs with relevant and solution-focused
leadership attributes to successfully lead teams, strengthen their organizations culture, solve problems
collaboratively, and expand their understanding of the Air Force’s role in joint operations to achieve national
strategic objectives. The NCOA meets these goals by providing the best academic program possible through the
delivery of outcome-based objectives related to the curriculum areas of Team Leadership, Joint Warfighting, and
Strategic Thinking. A self-study version of the NCOA program is available through Air University’s Global College
of PME to facilitate EPME completion for Air National Guard and Air Force Reserves members for whom resident
attendance may not be possible.
Noncommissioned Officer Foundations Course 500 (NCOFC500). NCOFC500 replaces the base level NCO
Professional Enhancement Seminar and will be a prerequisite for the Noncommissioned Officer Academy. The
course provides students with the skills and knowledge needed to lead by setting the example. It also enhances the
students’ capacity to continually advance factors that shape organizational culture, offer guidance that empowers
students to reflect on their behaviors in relation to the Airmen Leadership Qualities and facilitate students’
comprehension of techniques that contribute to establishing robust networks. The NCOF500 assists students in
grasping the connection between attention to detail, establishing impactful communication and fostering a culture of
trust. It promotes the realization that asking the appropriate questions involves understanding how to utilize the
answers effectively.
Operational Flying Duty Accumulator (OFDA). Aggregate months of flying duty performed under competent
orders while serving in assignments in which flying skills are maintained in the performance of assigned duties.
Resource Constraints. Resource deficiencies, such as money, facilities, time, workforce, and equipment that
preclude desired training from being accomplished.
Retraining. An Air Force objective to balance the career force of each AFSC as needed. The retraining program
allows individual airmen a choice of career fields from which to pursue an Air Force career and provides a method to
return Airmen disqualified from their current AFSC to a productive status.
Senior Noncommissioned Officer Academy (SNCOA). SNCOA provides professional military education to
prepare SNCOs to strengthen organizational leadership strategies and leverage national, military and airpower
strategies. Additionally, SNCOs will understand strategic competition and how integrated deterrence is important to
national security. SNCOA is 195 hours of guided discussion, experiential exercises, individual and group research,
formal lecture and concludes with a wargame scenario. The course deliberately prepares and advances SNCOs to
think critically & strategically and be relevant in their operating environment. Students who complete this course are
prepared for increased leadership responsibility in the joint, combined and interagency operating environment.
Senior Noncommissioned Officer Foundations Course 700 (SNCOFC700). SNCOFC700 replaces the base level
SNCO Professional Enhancement Seminar and will be a prerequisite for the Senior Noncommissioned Officer
Academy. The course provides students with the foundational skills and knowledge needed to develop, advise, and
lead teams successfully, and facilitates technical expertise for transitioning from first-line supervisors and trainers to
leaders of teams. The SNCOFC700 assists students in engaging in strategic leadership at the 9-skill level, offering a
rich arsenal of influence tactics for changing people’s viewpoints and behaviors. It assists students in learning how
to build and maintain social relationships to maximize their informal power and influence in an organization. The
course goes beyond managing into a proactive stance that will take the organization forward.
Specialty Training Standard (STS). An AF publication that describes an AFSC in terms of tasks and knowledge
an airman in that specialty may be expected to perform or to know on the job. It further serves as a contract between
AETC and the functional user to show which of the overall training requirements for an AFSC are taught in formal
schools and correspondence courses.
CFETP 1A1XX
9
Standard. An exact value, a physical entity, or abstract concept, that the appropriate authority, custom, or common
consent sets up and defines to serve as a reference, model, or rule in measuring quantities or qualities, developing
practices or procedures, or evaluating results. A fixed quantity or quality.
Subject Matter Expert (SME). An individual qualified in a particular specialty and who is consulted with their
subject matter expertise or knowledge of the specialty.
Survival, Evasion, Resistance, and Escape Training (SERE). Conducts preparedness training as part of a
supporting or supported force to survey areas for evasion, recovery corridors, contact sites, potential cache site
establishment, areas of interest and physical infrastructure.
Syllabus. Published outline of training required to achieve the proficiency specified in the course training standards
for a specific course. It prescribes the course content, instructions to conduct the training, and the approximate time
necessary to successfully complete all requirements. A formal syllabus may be published to include IQT, MQT, CT,
and other aircrew training as determined by the training command, MAJCOM, or unit. (Formal and standardized
syllabus are used primarily in AETC formal or developed courses.)
Total Force (TF). All collective Air Force components (active duty, reserve, guard, and civilian elements) of the
United States Air Force.
Unit Type Code (UTC). Compose the basic building blocks used in joint force planning and force packaging
methodology. UTCs may contain both manpower and equipment details, only manpower force elements, or required
equipment only. Air Force planners use UTCs to document total personnel and logistics requirements needed to
support operational planning and execution activities. (See AFFORGEN)
Unqualified [Crew Position] (UXX). Students in upgrade training for the duties of a specific crew position and must
be supervised by an instructor.
Upgrade Training (UGT). Mandatory training that leads to attainment of a higher qualification or certification.
Utilization and Training Workshop (U&TW). A forum consisting of the AFCFM, MFMs, SMEs, and AETC
training personnel who determine career field training requirements.
Weapons System Training Package (WSTP). An instructional course that includes IQT, MQT, and CT designed
for use at the unit to qualify or aid qualification in a duty position, program, or on a piece of equipment. The WSTP
may be printed, computer based, flying, simulator, or other audiovisual material.
CFETP CEA
10
SECTION A - General Information
1. Purpose
This CFETP provides information necessary for the AFCFM, MFMs, commanders, training managers, supervisors,
and instructors to plan, develop, manage, and conduct an effective and efficient career field training program. This
plan outlines training CEAs must receive to develop and progress throughout their aviation career. For the purpose
of this CFETP, training is divided into three areas: E-UFT, IQT, and MQT. The E-UFT phase is the AFS specific
training a CEA candidate receives via the Enlisted Training Model upon entry into the Air Force or upon retraining
into the CEA career field. The CEA CoE and, as required, the 558
th
Flying Training Squadron (FTS), are the E-UFT
segments for all TF CEA candidates in the AFS awarding process; all training thereafter is considered graduate level
training. SERE training is normally completed prior to IQT. CEAs may postpone SERE training until MQT;
however, if required, it is a prerequisite for attaining MR/CMR certification. After E-UFT, CEAs attend IQT
culminating with a successful AF Form 8/8A and award of a 3-skill level. Finally, CEAs enter the MQT phase, that
may also culminate in an additional AF Form 8/8A and unit commander certification, award of the 5-skill level, and
designated as MR/CMR. MQT can be completed in conjunction with an IQT syllabus at a FTU or within their
assigned operational unit. The award of a 7-skill level is automatically awarded when assigned to a Unit Manning
Document in a 7-level position or IAW grade requirements (unless previously qualified 7-level in another CEA
specialty) and the 9-skill level after promotion to SMSgt. Note: The conventional On-the-Job Training (OJT), UGT,
and CT construct does not apply to the CEA career field.
The CFETP has several purposes:
1.1.
Serves as a management tool to plan, manage, conduct, and evaluate a career field training program.
1.2.
Identifies task and knowledge training requirements and recommends education and training for each skill level
and phase of an individual’s career in the AFS.
1.3.
Lists training courses available in the specialty, identifies sources of training, and the training medium.
1.4.
Identifies major resource constraints that impact full implementation of the desired career field training
program.
2. Uses
The CFETP will be used by MFMs and supervisors at all levels to ensure comprehensive and cohesive training
programs are available and/or instituted for all Airmen in the specialty.
2.1.
AETC training personnel will develop and revise formal resident, non-resident, field, and ET based on
requirements established by the user and documented in Part II of the CFETP. The lead command MFM will
coordinate with the AFCFM to develop acquisition strategies for obtaining resources needed to provide the identified
training.
2.2.
MFMs will ensure their flight training programs compliment the CFETP, mandatory E-UFT, IQT, and MQT
requirements. MAJCOM-developed training to support the AFSC must be identified for inclusion in this plan and
must not duplicate available training resources.
2.3.
All CEA Airmen will complete mandatory training requirements specified in this plan. The list of courses in Part
II will be used as a reference to support training.
2.4.
Personnel serving as CEAs are exempt from maintaining OJT, DAF Form 623, Individual Training Record
Folder. Training is documented IAW AFMAN 11-202V1, Aircrew Training, AFMAN 11-2MDSV1 (Aircrew
Training, MDS specific), IQT syllabi, or other weapons system training guidance. AF Form 8/8A certifies an Aircrew
Qualification and flight evaluations are administered by flight examiners. Qualification on the AF Form 8/8A
eliminates the requirement to document STS items in this CFETP.
CFETP CEA
11
3. Coordination and Approval
The AFCFM is the approval authority. MFMs and AETC training managers will identify and coordinate on the career
field training requirements. The AFCFM will initiate an annual review of this document and coordinate with AETC
and MFMs to ensure currency and accuracy. Training managers will send applicable inputs/changes to CEA MFMs
via CRM when initiated annually. CEA MFMs will then consider inputs/changes to be routed to HQ USAF/A3TS
at [email protected] when requested.
SECTION B - Career Progression and Information
4. Specialty Descriptions This information supplements the AFECD. AFSC specific descriptions can be found in
the AFECD. Duties and Responsibilities:
4.1 1A1X2 Mobility Force Aviator (MFA) MFAs are experts in conducting inter and intra-theater airlifts of
personnel and materiel, as well as planning and executing theater air refueling for fixed-wing aircraft as Loadmasters,
Flight Engineers and Boom Operators, specializing in Rapid Global Mobility and Global Reach mission execution.
Additionally, MFAs conduct ground refueling operations, serve as refuel panel operators, refueling supervisors, and
concurrent servicing supervisors. Their primary role during mission planning involves calculating Takeoff and
Landing Data (TOLD) to ensure safe and optimal aircraft performance at departure and arrival airfields. They are
also responsible for determining aircraft climb, cruise, and descent performance parameters, while frequently
accounting for factors, such as operation from unprepared surfaces, inclement weather, and obstacle avoidance.
MFAs may also be responsible for cargo/passenger loading and unloading activities, computes aircraft weight and
balance, and performs aircrew functions and other mission specific qualification duties to include the airdrop of
personnel and equipment/cargo. During pre-flight and post-flight inspections, MFAs ensure the adequacy of cargo
documentation, execute normal and emergency procedure checklists, and operate and monitor engine, hydraulic,
fuel, pneumatic, and other aircraft systems controls throughout all phases of ground and flight operations, performing
in-flight refueling aircrew functions and activities according to flight manuals, checklists, and United States Air
Force publications. MFAs execute a wide range of critical tasks, including combat offloads, airdrop operations,
Forward Arming and Refueling Point (FARP) support, tactical NVG (Night Vision Goggles) low-level flight, and
air refueling. Their duties include, but are not limited to, the coordination of post-mission aircraft maintenance and
servicing requirements during enroute stops and upon returning to the home station.
4.2 1A1X3 Special Mission Aviator (SMA) Special Mission Aviators (SMA) are tasked with a diverse array of
responsibilities across various aircraft types, including fixed-wing, rotary-wing, and tilt-rotor encompassing Special
Operations, Close Air Support, Combat Search and Rescue, Personnel Recovery, Nuclear Security, and Domestic
Security. They serve as Flight Engineers, Loadmasters, and Aerial Gunners. In potentially hostile environments,
Special Mission Aviators (SMAs) execute a wide range of critical tasks, including combat offloads, airdrop
operations, Forward Arming and Refueling Point (FARP) support, tactical NVG (Night Vision Goggles) low-level
flight, air refueling, infiltration/exfiltration missions, alternate insertion/extractions, aerial gunnery, and respond to
emergency procedures. Moreover, SMAs manage aircraft radios, operate communication equipment, and fulfill joint
airdrop inspector duties, ensuring mission success across diverse operational situations. Their duties include, but are
not limited to, conducting pre- and post-flight inspections, cargo and personnel on/offloading, monitoring aircraft
systems, servicing aircraft in remote locations, and contributing significantly to mission planning efforts.
4.3 1A1X4 Multi-domain Operations Aviator (MOA) Multi-domain Operations Aviators (MOAs) specialize in
electromagnetic spectrum operations (EMSO), airborne communications, datalinks, radar systems, and kinetic
strikes, including terminal guidance of munitions, as systems operators and airborne network systems administrators
on various Command, Control, Communications and Computers Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance
(C4ISR) platforms. Serving as mission crewmembers on airborne platforms or remotely piloted aircraft (RPA),
MOAs gather, record, display, and distribute mission information. They utilize airborne sensors to acquire, track,
and monitor airborne, maritime, and ground objects to interpret computer-generated displays and alarms for safe
mission execution. MOAs are responsible for the maintenance and operation of mission equipment, electronic attack
(EA), and electronic protection (EP) equipment to optimize the performance of airborne and ground systems. MOAs
quickly field, integrate and operationalize new airborne equipment and capabilities. Additionally, MOAs support
other airborne and ground entities by distributing and relaying operational target and identification data. They
monitor aircraft and weapons systems status to ensure efficient airpower application and respond to emergency
procedures onboard aircraft when necessary. MOAs are experts in troubleshooting to repair airborne and ground-
based systems to manage operating and maintenance functions. MOAs maintain operational inspection maintenance

CFETP CEA
12
records and documents while addressing infrequent equipment operation and in-flight maintenance issues. Their
duties include, but are not limited to, pre-flight, in-flight, and post-flight operations, including operating,
maintaining, repairing, and testing airborne communication systems, electro-optical sensor systems, and computer
systems.
4.4 1A1X8 Executive Mission Aviator (EMA) EMAs are integral to safe and reliable executive airlift operations
in support of military and civilian leaders, including the President, Vice President, Secretary of Defense, Chairman
of the Joint Chief of Staff, First Lady, Congressional Delegations, and Combatant Commanders. Trained in diverse
aircrew roles such as Flight Attendant, Flight Engineer, and Communication Systems Operator, EMAs undertake a
spectrum of responsibilities crucial to flight operations. Their duties include, but are not limited to, executing mission
planning and coordination of in-flight meals, passenger service, and comfort requirements, managing luggage and
passenger loading, executing normal and emergency procedure checklists, operating and monitoring engine,
hydraulic, fuel, and other aircraft systems throughout all phases of ground and flight operations as well as
maintaining and operating voice and data communications networks onboard a variety of airborne platforms.
5. Training Decisions
The CFETP uses a building block approach (simple to complex) to encompass the entire spectrum of training
requirements for the CEA specialty. This CFETP was developed to include life cycle (day one through retirement)
training requirements for this specialty. The spectrum includes a strategy for when, where, and how to meet the
training requirements. The strategy must be apparent and affordable to reduce duplication of training and eliminate a
disjointed approach to training.
5.1.
Enlisted Undergraduate Flying Training. Initial physiological training will be conducted at the CEAFC. The
STS is used to align common core training across all 1A1XX/ Sub-IDs. Award of the 3-level will be earned by
successful completion of IQT and initial AF Form 8/8A.
6. Community College of the Air Force (CCAF) Academic Programs
CCAF provides the opportunity to obtain an Associate in Applied Science (AAS) Degree. Enrollment in CCAF
occurs upon completion of BMT. All CCAF accredited E-UFT courses award credit towards applicable AAS Degree
to that specialty. See the CCAF General Catalog, located on the Air University website for program details regarding
the AAS degree at: https://www.airuniversity.af.edu/Barnes/CCAF/. Additionally, see the Air Force Virtual
Education Center website regarding AAS degree progress at: https://afvec.us.af.mil/afvec. In addition to its associate
degree programs, CCAF offers the following certifications and degree opportunities:
6.1.
CCAF Instructor Certification. The CCAF offers the CCAF Instructor Certification to qualified instructors
who teach CCAF collegiate-level credit-awarding courses at a CCAF affiliated school. The CIC is a professional
credential that recognizes the instructor’s extensive faculty development training, education, and qualification
required to teach a CCAF course. It also formally acknowledges the instructor’s practical teaching experience.
Qualified CCAF instructors who meet CIC Program requirements are eligible. Once instructors leave CCAF
instructor duty, they are no longer eligible for the CIC program.
6.2.
Instructor of Technology & Military Science Degree. This program is offered to enlisted members who are
assigned to CCAF affiliated schools teaching CCAF degree-applicable courses. Applicants must complete three
semester hours of CCAF-approved instructor methodology coursework and hold their career field related CCAF
degree or equivalent civilian college degree before registration.
6.3.
Trade Skill Certification. When a CCAF student separates or retires, a trade skill certification is awarded for
the primary occupational specialty. The College uses a competency-based assessment process for trade skill
certification at one of four proficiency levels: Apprentice, Journeyman, Craftsman/Supervisor, or Master
Craftsman/Manager. All are transcribed on the CCAF transcript.
6.4.
Degree Requirements. All Airmen are automatically entered into the CCAF program. Refer to the CCAF
General Catalog for the applicable degree program that applies to your CEA specialty. Prior to completing an
associate degree, the 5-skill level must be awarded and the following requirements in the CCAF General Catalog.
6.4.1.
For current AFSC Sub–ID Degree Requirements, please visit the below link to read the CCAF General Catalog:
https://www.airuniversity.af.edu/Portals/10/CCAF/documents/2022-2024_CCAF_General_Catalog- Change1.pdf

CFETP CEA
13
6.4.2.
Additional off-duty education is a personal choice that is encouraged for all. Individuals desiring to become an
Air Education and Training Command Instructor should be actively pursuing an associate degree. A degreed faculty
is necessary to maintain accreditation through the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools.
6.5.
Assignments. See Talent Marketplace for current list of CEA assignment locations.
6.5.1.
Talent Marketplace https://myvector.us.af.mil/myvector/Talentmarketplace/Home.
6.5.2.
Air Force Reserve: https://afmilpers.us.af.mil/RMVSNet40/SelectVacancies.aspx.
6.5.3.
Air National Guard: https://intelshare.intelink.gov/sites/ngbhr/careers/SitePages/State-
Unit%20Vacancies.aspx
7. Career Field Flow Charts
7.1.
The flow outlined in Figure 1 and courses in Tables 2 through 10 represent the formal training courses required
for personnel entering and becoming fully qualified in the CEA AFSC. A focus on experience and competency early
in their careers will help CEAs chart and achieve many of their individual and professional Air Force career goals.
Consequently, education, training and experience should complement one another to develop Airmen with
theoretical and practical mastery of aviation management principles. The career path charts in Figure 1 and Tables 2
through 10 display CEA career progression with multiple paths and developmental opportunities within these
specialties. The locations, course lengths, and titles are MDS dependent, and are subject to change. Changes will be
updated in the Education Training Course Announcement (ETCA) by the course owner.
7.2.
The course flow has been developed and agreed upon by the MFMs to minimize days students are awaiting
training and to ensure survival training is typically completed prior to AFSC award—minimizing the impact of not
having the prerequisites completed before entering weapons system training.
7.3.
Personnel graduating from the E-UFT FTU Preparatory courses at the CEA CoE and the 558th FTS are awarded
AFSC 1A11X and are temporarily authorized to wear the Basic Aircrew Member Badge. CEA candidates are not
authorized to continue wear of the Airman Aircrew Badge if they fail to complete IQT or disqualified prior to 18
months of aviation service IAW AFMAN 11-402, Aviation and Parachutist Service Aeronautical Ratings and
Badges.
CFETP CEA
14
Table 1. Enlisted Education and Training Path
Enlisted Education and Training Path
Education and Training
Requirements
GRADE REQUIREMENTS / AVERAGES
Rank
Earliest
Sew-on
Air Force
Average
MFA
Average
SMA
Average
EMA
Average
MOA
Average
High
Year
of
Tenure
(HYT)
Basic Military Training School
(BMTS)
Undergraduate Flying Training
Amn
6 months
Graduate Flying Training (3-Skill
Level)
A1C
10 months
Upgrade To Journeyman (5-Skill
Level)
Completion of Mission Qualification
Training or MR/CMR Status
SrA
28
months
3 years
3 years
3 years
3 years
3 years
10
years
Junior Enlisted Foundations
Course 300 (JEFC300)**
Airman Leadership School (ALS)*
- Resident graduation is a prerequisite
for SSgt sew-on (RegAF Only)
Upgrade To Craftsman (7-Skill
Level)
SSgt
3 years
5.10 years
4.42 years
4.86 years
4.24 years
4.36 years
20
years
- 12 months Fully Mission Qualified
(6 months for retrainees)
NCO Foundations Course 500
(NCOFC500)**
TSgt
5 years
8.83 years
8.84 years
9.48 years
8.57 years
8.39 years
22
years
NCO Academy (NCOA)*
- Must be a TSgt or TSgt-select to
attend (SSgts may attend if all class
seats have not been filled)
Resident graduation is a prerequisite
for MSgt sew-on (RegAF Only)
SNCO Foundations Course 700
(SNCOFC700)**
MSgt
8 years
13.82
years
14.42
years
14.22
years
14.12
years
14.28
years
24
years
Senior NCO Academy (SNCOA)*
Must be a SMSgt, SMSgt select, or
Non-selects to SMSgt across AFSCs
Upgrade to Superintendent (9-Skill
level)
SMSgt
11 years
17.88
years
16.82
years
18.49
years
18.72
years
16.82
years
26
years
- Minimum rank of SMSgt
Chief Leadership Course (CLC)
CMSgt
14 years
21.00
years
20.12
years
20.36
years
21.25
years
19.88
years
30
years
-Required for re-enlistment and
development opportunities
-Must be a CMSgt or CMSgt Select to
attend
- Completed SNCO Academy (RegAF
Only)
*ARC personnel may satisfy EPME requirements via Distance Learning
**Will become prerequisite courses for EPME in FY25
Data reflects Promotion cycle 23E5-9. MFA averages include 1A0, 1A1, and 1A2. SMA averages include 1A2 and 1A9. EMA averages
include 1A1, 1A3, and 1A6. MOA averages include 1A3 and 1U0.
CFETP CEA
15
SECTION C – Skill Level Training Requirements
8. Purpose
Skill level training requirements in this career field are defined in terms of task and knowledge requirements. This
section outlines the specialty qualifications requirements for each skill level in broad, general terms and establishes
the mandatory requirements for entry, award, and retention of each skill level. The specific task and knowledge
training requirements are identified in the STS and the Course Objective List Part II, Section A and B of this CFETP.
9. Skill Level Training.
9.1.
Apprentice 3-Level Training.
9.1.1.
Specialty Qualification.
9.1.1.1.
Knowledge. Knowledge requirements for awarding of the 3-skill level are satisfied by completing the
CEAFC, the Sub-ID specific E-UFT course at the CEA CoE and/or the 558th FTS and completing MDS-specific
IQT with a successful AF Form 8/8A.
9.1.1.2.
Education. For entry into this specialty, completion of high school courses in science, technology,
engineering, and mathematics are desirable.
9.1.1.3.
Training. For award of the 1A13X, individuals must meet mandatory requirements listed in specialty
description in AFECD. Completion of the CEAFC is mandatory for pipeline and non-prior aviation service cross
training students. Completion of the necessary E-UFT courses at the CEA CoE and/or the 558th Flying Training
Squadron and IQT with a successful AF Form 8/8A is mandatory for award of the 3-skill level AFSC.
9.1.1.3.1.
Qualification for aviation service according to AFMAN 11-402.
9.1.1.3.2.
Eligibility for a Secret security clearance minimum. Some specialties require eligibility for a Top-Secret
security clearance according to AFMAN 16-1405, Air Force Personnel Security Program.
9.1.1.3.3.
Completion of SERE and Water Survival Training Course(s) is mandatory for all CEAs performing in-
flight duties.
9.1.1.4.
Training Sources. Completion of an appropriate E-UFT course at the CEA CoE within the 344th Training
Squadron satisfies the knowledge and training requirements specified in the specialty qualification section (above)
for continued flight training. Completion of the first AF Form 8/8A awards the 3-skill level.
9.1.1.5.
Implementation. Entry into training is accomplished by initial accessions from BMT or approved retraining
from any AFSC. After graduation from E-UFT, IQT begins when the individual enters formal flight training.
Thereafter, in-unit or formal upgrade training is initiated anytime an individual is assigned duties they are not
qualified to perform.
9.2.
Journeyman 5-Level Training.
9.2.1.
Specialty Qualification. All qualifications for the 3-skill level apply to the 5-skill level requirements.
9.2.2.
Knowledge. Knowledge requirements for awarding the 5-skill level are satisfied after completing MQT that
results in commander’s MR/CMR certification and or a successful Mission Qualification AF Form 8/8A, as required.
CFETP CEA
16
9.2.3.
Education. To assume the rank of SSgt, the individual must be a graduate of ALS.
9.2.4.
Training. The following training is mandatory for the award of the 5-skill level: Complete unit level MQT
that results in MR/CMR certification and or a successful Mission Qualification AF Form 8/8A.
9.2.5.
Experience. Qualification in and possession of a 3-skill level. In addition, the individual must complete
requirements as listed in the applicable MAJCOM aircrew training directives, IQT with a successful AF Form 8/8A,
and MQT.
9.2.6.
Training Sources. Refer to Part II, Section D, Training Course Index.
9.2.7.
Implementation. Entry into upgrade training is initiated when an individual possesses the 3-skill level.
Qualification training is initiated anytime an individual is assigned duties they are not qualified to perform.
9.3.
Craftsman 7-Level Training.
9.3.1.
Specialty Qualification.
9.3.2.
Knowledge. In addition to knowledge required for the 5-skill level and other qualifications as listed above an
individual must possess the knowledge and skills necessary to supervise personnel.
9.3.3.
Education. To assume the grades of SSgt and MSgt, individuals must be graduates of the ALS and NCOA,
respectively. Reference DAFI 36-2670, Total Force Development.
9.3.4.
Training. There is no requirement for in-residence 7-skill level training for all CEA career fields. However,
minimum rank of SSgt and recommendation by the supervisor still apply.
9.3.5.
Experience. Qualification in and possession of 5-skill level. Also, 12 months fully mission qualified.
9.3.6.
Training Sources. Refer to Part II, Section D, Training Course Index.
9.4.
Superintendent 9- Level Training.
9.4.1.
Specialty Qualification
9.4.2.
Knowledge. In addition to knowledge required for the 7-skill level qualification, an individual must possess
advanced skills and knowledge of concepts and principles in the effective leadership of CEAs in multiple disciplines
and management of assigned resources.
9.4.3.
Education. Completion of SNCOA (RegAF – In-Residence, ARC – In-Residence or DL) commensurate with
rank requirements. Additionally, award of the CCAF AAS degree or an associate degree or higher from a nationally
or regionally accredited academic institution, if not already earned, is recommended.
9.4.4.
Training. Must hold the rank of SMSgt and have supervisor’s recommendation for award of the 9-skill level
(RegAF only).
9.4.5.
Experience. Qualification in and possession of a 7-skill level. Also, experience managing advanced operations
and maintenance of aircraft mission systems.
CFETP CEA
17
Section D - Resource Constraints
10. Purpose
This section identifies known resource constraints that preclude optimal/desired training from being developed or
conducted, including information such as cost and workforce. Narrative explanations of each resource constraint and
an impact statement describing what effect each constraint has on training are included. Also included in this section
are actions required, office of primary responsibility, and target completion dates. Resource constraints will be
reviewed and updated at least annually.
11. Apprentice 3-Level Training
CEAs train and qualify on USAF MDS aircraft via IQT and MQT. IQT quotas are programmed via the Aircrew
Training Distribution Requirements (ATDR) process outlined in DAFI 11-412, Aircrew Management. Rated officer
production programming is accomplished using the ATDR process. ATDR is programmed two fiscal years prior to
the year-of-execution as part of the Program Objective Memorandum (POM) and Future Years Defense Program
(FYDP) build.
12. Journeyman 5-Level Training
CEAs train and certify as MR/CMR via a MQT program completed at the FTU or in their assigned operational unit.
MQT throughput is determined by the USAF Flying Hour Program (FHP).
13. Craftsman 7-Level Training
There is no requirement for in-residence 7-skill level training for all CEA career fields. However, minimum rank of
SSgt and recommendation by the supervisor still apply.
3 Attachments:
1.
Qualitative Requirements
2.
STS by sub-ID (CEA)
3.
CFETP Career Path Chart (CEA)
BY ORDER OF THE SECRETARY OF THE AIR FORCE
OFFICIAL TRAVOLIS A. SIMMONS, Brig Gen, USAF
Director, Training and Readiness

CFETP CEA
18
PART II
SECTION A – Specialty Training Standards (STS)
1. Implementation
This STS will be used for technical training provided by AETC for classes beginning October 2024.
2. Purpose
As prescribed in DAFMAN 36-2689, Enlisted Force Development, and this STS.
2.1.
List in column 1 (Task, Knowledge, and Technical Reference) the most common tasks, knowledge, and technical
references (TR) necessary for airmen to perform duties at the 3-skill level AFSC in the CEA Specialty ladder of the
Aircrew Operation Career Field. These are based on the analysis of the duties in AFECD.
2.2.
Column 2 (Standard) shows formal training and correspondence course requirements as described in the ETCA
website at: https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx?isdlg=1 and the career knowledge provided
by the correspondence course. There are no Career Development Courses listed for this AFSC.
2.3.
Qualitative requirements contained in Attachment 1 defines the proficiency code key used to indicate the level
of training and knowledge provided by resident training and career development courses.
2.4.
Utilized as a guide for development of promotion tests used in the Weighted Airmen Promotion System
(WAPS). Specialty Knowledge Tests (SKTs) are developed at the USAF Occupational Measurement Squadron by
SNCOs with extensive practical experience in their career fields. The tests sample knowledge of STS subject matter
areas judged by test development team members to be most appropriate for promotion to higher grades. Questions
are based on study references listed in the WAPS study catalog. Individual responsibilities are in AFMAN 36-2664,
Personnel Assessment Program.
SECTION B – Course Objective List
3. Measurement
Each objective is indicated as follows: W indicates task or subject knowledge, which is measured using a written
test, PC indicates required task performance which is measured with a performance check, and PC/W indicates
separate measurement of both knowledge and performance elements using a written test and a performance progress
check.
4. Standard
The minimum passing score on written examinations is 85% to match aircrew standards outlined in the 11-202V2
regarding periodic testing examinations. Standards of performance measurement are indicated in the objective and
delineated on the individual progress checklist. Instructor assistance is provided and needed during the progress
check, and students may be required to repeat all or part of the behavior until satisfactory performance is attained.
5. Proficiency Level
Most task performance is taught to the “1a” proficiency level which means the students can do simple parts of the
task but needs to be told or shown how to do most of the task (extremely limited) or to a “2b” proficiency level
which means the students can do most parts of the task but does need assistance on the hardest parts of the task
(partially proficient). The student can also determine step-by-step procedures for doing the task.
6. Advanced Course Skills
Note: There are no advanced courses for CEAFC or FTU Preparatory Courses.
CFETP CEA
19
SECTION C – Support Material
7. Support Materials
Note: There are currently no support material requirements.
SECTION D – Training Course Index
8. Purpose
This section of the CFETP identifies training courses available for the specialty and shows how the courses are used
by each MAJCOM in their career field training programs.
Table 2. MFA Air Force In-Residence Courses
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
L3AQ1A112 01AA
Career Enlisted Aviator Fundamentals Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB,
TX
L3AQR1A112 01BA
Mobility Force Aviator FTU Preparatory Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB, TX
S-V97-A
Advanced SERE Skills Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
S-V85-A
Emergency Parachute and Water Survival Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
KC135BIQ
KC-135 Boom Operation Initial Qualification Course
Altus AFB, OK
KC135BTX2
KC-135 Boom Operator Requalification Course
Altus AFB, OK
KC135IB
KC-135 Instructor Boom Operator Qualification
Altus AFB, OK
BO AIC
KC-135 Advanced Instructor Course
Fairchild AFB, WA
KC46BIQ
KC-46 Boom Operator Initial Qualification Course
Altus AFB, OK
KC46BTX
KC-46 Boom Operator Transition Course
Altus AFB, OK
KC-46BRC
KC-46 Boom Operator Requalification Course
Altus AFB, OK
KC46IB
KC-46 Instructor Boom Operator Course
Altus AFB, OK
C5MFEIQ
C-5M Flight Engineer Initial Qualification
JBSA-Kelly AFB, TX
C5MIFE
C-5M Instructor Flight Engineer Qualification
JBSA-Kelly AFB, TX
C5MLIQ
C-5 Loadmaster Initial Qualification Course
JBSA-Kelly AFB, TX
C17LIQ
C-17 Loadmaster Initial Qualification
Altus AFB, OK
C17ILM
C-17 Instructor Loadmaster Qualification Course
Altus AFB, OK
C17LAD
C-17 Loadmaster Airdrop Course
Altus AFB, OK
CFETP CEA
20
C-17 LM AIC
C-17 Loadmaster Advanced Instructor Course
JB Lewis-McChord, WA
C17LTX-4
C-17 Loadmaster Transition Course
Altus AFB, OK
C130H2FEQ1LP
C-130H2 Flight Engineer Initial Qualification (Basic)
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130H2FEQ3LP
C-130H2 Flight Engineer Initial & Mission Qualification
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130H2FIN3LP
C-130H2 Flight Engineer Instructor
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130H2LMQ1LP
C-130H2 Loadmaster Initial Qualification Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130H2LMQ3LP
C-130H2 Loadmaster Initial/Mission Qualification
Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLIQ1LP
C-130J Loadmaster Initial Qualification
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLIQ3LP
C-130J Loadmaster Initial/Mission Qualification Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130H2LIN3LP
C-130 Loadmaster Instructor Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLIN3LP
C-130J Loadmaster Instructor Qualification Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLIQ5LP
C-130J Loadmaster Mission Qualification Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLXA3LP
C-130J Loadmaster Transition Long Course (Qual &
Msn)
Little Rock AFB, AR
C130JLXB3LP
C-130J Loadmaster Transition Short Course (Qual &
Msn)
Little Rock AFB, AR
C-130J LM AIC
C-130J Loadmaster Advanced Instructor Course
Little Rock AFB, AR
E-3G DMAE-IQT
E-3G Flight Engineer Initial Qualification Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E-3G DMAE-IUT
E-3G Flight Engineer Instructor Upgrade Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E-3 DCT
E-3 DRAGON Conversion Training Combined Pilot/FE
Course
Tinker AFB, OK
NOTE: Please check Education & Training Course Announcements for the most updated Course Number and
information:
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
Table 3. Air Mobility Command Distance Learning Courses
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
DL RGMC1
Rapid Global Mobility Course I
https://lms-jets.cce.af.mil
DL RGMC II
Rapid Global Mobility Course II
https://lms-jets.cce.af.mil
WBT AF FEMO
AF Fundamentals of Expeditionary Mobility Operations
https://lms-jets.cce.af.mil
WBT STAGE
Stage Management Course
https://lms-jets.cce.af.mil
Table 4. MFA Advanced Training
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
AATTC
Advanced Airlift Tactics Training Center Course
St. Joseph ANGB, MO
AMC CATS\MECOC
Combat Aircrew Tactics Studies (CATS) and Mobility
Electronic Combat Officer Course (MECOC)
St. Joseph ANGB, MO
S-V84-A
USAF Underwater Egress Training (UET)
Fairchild AFB, WA
CFETP CEA
21
Table 5. EMA Air Force In-Residence Training
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
L3AQR1A118 01AA
Career Enlisted Aviator Fundamentals Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB, TX
L3AQR1A118 01BA
Executive Misson Aviator FTU Preparatory Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB, TX
S-V97-A
Advanced SERE Skills Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
S-V85-A
Emergency Parachute and Water Survival Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
C-37A/B FDQ
C-37A/B Flight Engineer Differences Training
Andrews AFB. MD
C37A FMX
C-37A (G-5) Flight Engineer Initial Maintenance Course
Flight Safety International
C37A FIQ
C-37A Flight Engineer Initial Qualification
Flight Safety International
E4BAMSS-CORE
E-4B Common Core Academics
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-DATA
E-4B DATA Communications Operator Qual/Requal
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-VO
E-4B Voice Operator, Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-RO
E-4B Radio Operator Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-TC1
E-4B Tech Controller #1 Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-TC2
E-4B Tech Controller #2 Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-CSO
E-4B Comm Sys Operator Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-RM
E-4B Radio Maintenance Op Qualification & Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BAMSS-WIRE
E-4B Dual Trailing Wire Antenna Operator Qual/Requal
Offutt AFB, NE
E4B - Flt Attend
E-4B Flight Attendant Initial Qual, Requal, and Instructor
Upgrade
Offutt AFB, NE
E4BIFE
E-4B IFE Qualification & Requalification Course
Offutt AFB, NE
E4FE
E-4B Flight Engineer Qualification & Requalification Course
Offutt AFB, NE
NOTE: Please check Education & Training Course Announcements for the most updated Course Number and
information:
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
Table 6. EMA Contracted Training
PROVIDER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
Flight Safety
Emergency Egress Simulator <20 Passengers
Savannah, GA
ATLAS
Emergency Egress Simulator >20 Passengers
Miami, FL
MedAire, Inc.
In-flight Emergency Medical Training
Local
Table 7. SMA Air Force In-Residence Courses
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
L3AQ1A113 01AA
Career Enlisted Aviator Fundamentals Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB,
TX
L3AQR1A113 01BA
Special Mission Aviator FTU Preparatory Course -
Undergraduate Flying Training
JBSA-Lackland AFB, TX
S-V97-A
Advanced SERE Skills Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
S-V85-A
Emergency Parachute and Water Survival Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
CFETP CEA
22
S-V84-A
USAF Underwater Egress Training (UET)
Fairchild AFB, WA
E-A9H-A
TH-1H Career Enlisted Aviator Rotary-Wing Fundamentals
Course (CEARF)
Fort Novosel, AL
E-I9H-A
TH-1H Special Missions Aviator Instructor Training
(SMAIT)
Fort Novosel, AL
CV22-SMA-IQ
CV-22 Special Missions Aviator Initial Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
CV22-IP/F-UQ
CV-22 Instructor Pilot/Flight Engineer Upgrade Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
HH60G-SMAI-UQ
HH-60G Special Missions Aviator Instructor Upgrade
Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
HHW1A9IMQ
HH-60W Special Missions Aviator Initial/Mission
Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
HHW1A9CV
HH-60W Special Missions Aviator Conversion Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
HHW1A9IU
HH-60W Fully Qualified Special Missions Aviator Instructor
Upgrade
Kirtland AFB, NM
HH-60 SMA AIC
HH-60 Special Missions Aviator Advanced Instructor Course
Nellis AFB, NV
UHN1A9IMQ
UH-1N Special Missions Aviator Initial Mission Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
UHN1A9IUQ
UH-1N Instructor Special Mission Aviator Upgrade
Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
UHN1A9TX1
UH-1N Special Missions Aviator Transition Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
UHN1A9TX2
UH-1N Special Missions Aviator Requalification Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
ACJ1A9IQ
AC-130J Loadmaster/Special Mission Aviator Initial And
Mission Qualification Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
AC130JAG
AC130J Aerial Gunner Mission Qualification
Hurlburt Field, FL
AC130JIAG
AC130J Instructor Aerial Gunner Mission Qualification
Hurlburt Field, FL
HCJ1A2I/MQ
HC-130J Loadmaster Initial & Mission Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
HCJ1A2IUQ
HC-130J Instructor Loadmaster Upgrade Qualification
Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
HCJ1A2PRTX
HC-130J Loadmaster Personnel Recovery Transition Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
MCJ1A2IMQ
MC-130J Loadmaster Initial & Mission Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
MCJ1A2IQ
MC-130J Loadmaster/Special Mission Aviator Initial
Qualification
Kirtland AFB, NM
MCJ1A2IUQ
MC-130J Instructor Loadmaster Upgrade Qualification
Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
MCJ1A2SOTX
MC-130J Special Operations Transition Course
Kirtland AFB, NM
C146-ML-IQ
C146A Loadmaster Initial Mission Qualification Course
Duke Field, FL
C146AILM
C146A Instructor Loadmaster Upgrade (ILUG) Course
Duke Field, FL
NOTE: Please check Education & Training Course Announcements for the most updated Course Number and
information:
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
CFETP CEA
23
Table 8. MOA Air Force In-Residence Courses
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
L3AQR1A311 01AC
Aircrew Fundamentals Course – Airborne Mission Systems
JBSA-Lackland
AFB,TX
TBD
Multi-domain Operations Aviator Course
JBSA-Randolph
AFB, TX
S-V97-A
Advanced SERE Skills Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
S-V85-A
Emergency Parachute and Water Survival Training
Fairchild AFB, WA
SERE 220
SPECIAL SURVIVAL TRAINING
Fairchild AFB, WA
SERE 245 FAFB
SPECIAL SURVIVAL TRAINING
Fairchild AFB, WA
E3 BQART
E-3 Airborne Radar Technician Initial Qualification Training
Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E-3G ADST-IQ
E-3G Airborne Data Systems Technician Initial Qualification
Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E-3G ARO-IQ
E-3G Airborne Radio Operator Initial Qualification Training
Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E-3G BQMSO
E-3G Mission Systems Operator Initial Qualification Training
Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E3IADST
E-3 Instructor Airborne Data Systems Technician (IADST)
Upgrade
Tinker AFB, OK
E3IARO
E-3 Instructor Airborne Radio Operator (IARO) Upgrade
Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E3IART
E-3 Instructor Airborne Radar Technician (IART) Upgrade
Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
E3IMSO
E-3 Instructor Mission Systems Operator (IMSO) Upgrade
Training Course
Tinker AFB, OK
TBD
E-11A Payload Operator Initial Qualification Course
Robins AFB, GA
MQ-9 SLFT
MQ-9 Senior Leadership Familiarization Training (SLFT)
Holloman AFB, NM;
Creech AFB, NV;
March ARB, CA;
MQ9FIUT
MQ-9 FTU Instructor Upgrade Training Course
Syracuse ANGB, NY
MQ9FIUT
MQ-9 FTU Instructor Upgrade Training Course
Holloman AFB,
NM; Creech AFB,
NV;
March ARB, CA;
Syracuse ANGB,
NY
MQ-9 SLQT
MQ-9 Senior Leadership Qualification Training (SLQT)
Holloman AFB, NM;
Creech AFB, NV;
March ARB, CA;
Syracuse ANGB, NY
MQ9IQT
MQ-9 Basic and Requalification Training Course (B/TX-1)
Holloman AFB, NM;
Creech AFB, NV;
March ARB, CA;
Syracuse ANGB, NY
MQ-9 SO AIC
USAF MQ-9 Sensor Operator Advanced Instructor Course
Nellis AFB, NV
MQ9PSOLRC
MQ-9 Launch/Recovery Training Course
Creech AFB, NV
MQ9LRIU
MQ-9 Launch and Recovery Instructor Upgrade
Creech AFB, NV
RC135VASE-1
RC-135V/W Airborne Systems Engineer 1 Qual, Requal, Diff,
Instr Qualification
Offutt AFB, NE
RC135VASE-3
RC-135V/W Airborne System Engineer 3 Qual, Requal, Diff,
Instr Qualification
Offutt AFB, NE
CFETP CEA
24
RC135VASE-5
RC-135V/W Airborne Systems Engineer 5 Qualification &
Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
RC135USASE-1
RC-135U/S Airborne Systems Engineer 1
Qual/Requal/Diff/Instructor Qualification
Offutt AFB, NE
RC135SASE2
RC-135S Airborne Systems Engineer 2 Qualification &
Requalification
Offutt AFB, NE
RC135UASE3
RC-135U Airborne Systems Engineer 3 Qual, Requal, Diff,
Instructor Course
Offutt AFB, NE
RQ4B40SOBQT
RQ-4 Sensor Operator Basic Qualification Training
Grand Forks AFB,
ND
RQ4ISOUG
RQ-4 Instructor Sensor Operator Upgrade Training
Grand Forks AFB,
ND
CCALLAMT
EC-130H Compass Call Airborne Maintenance Technician
(AMT)
Davis-Monthan
AFB, AZ
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
Table 9. Air Education and Training Command Courses
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
L3AIRTXXXX 0B1A
Basic Instructor Course (BIC)
JBSA-Lackland AFB, TX
E6AZU3S200 015
CDC Writer
CBT Course
E6AILTXXXX 011A
Principles of Instructional System Development
CBT Course
5ACC3S200-003
Academic Instructor Course (AIC)
JBSA-Randolph AFB, TX
394AIT3S20000AB
Principles of Instruction (POI)
Multiple
NOTE: Please check Education & Training Course Announcements for the most updated Course Number and
information:
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
Table 10. Career Enlisted Aviator Advanced Training
COURSE NUMBER
COURSE TITLE
LOCATION
S-V87-A
Arctic Survival Training Course
Eielson AFB, AK
JAOC2C
Joint Air Operations Command and Control
Course
Hurlburt Field, FL
L5AZA1A2510F5A
Airdrop Load Inspector Certification Course
Ft. Gregg-Adams, VA
ETC
Enlisted Test Fundamentals
Edwards AFB, CA
NOTE: Please check Education & Training Course Announcements for the most updated Course Number and
information:
https://usaf.dps.mil/teams/app10-etca/SitePages/home.aspx
Current as of 22 Jul 24
CFETP CEA
25
SECTION E – MAJCOM Unique Requirements
1.
Air National Guard (ANG)
1.1.
Purpose. This section applies to all CEA assigned to ANG units.
1.2.
Proficiency Training.
1.2.1.1.
Upon completion of the IQT, ANG CEAs require a minimum number of training days to become
MR/CMR and obtain operational proficiency as outlined in the most recent Ready Aircrew Program
(RAP) Tasking Message/MDS Vol 1. The number of days required for a member to attain CMR may be
adjusted accordingly by the ANG CEA CFM as required to meet all necessary requirements identified in
the MDS Vol 1 and applicable AFIs/supplements.
Table 11. ANG MR Training Days
Sub-ID
Days
1A1X2G/H
250
1A1X2L
250
1A1X2C/D/N
250
1A1X3B/E/F
365
1A1X4F
365
1A1X8A
240
1.2.2.
CMR, as defined in the RAP tasking message/MDS Vol 1, and proficiency training will include TDY
travel to accomplish training when not available at home station.
1.2.2.1.
ANG may hire Airmen who are not previously qualified CEAs into the EMA specialty upon CFM
approval. Approval will be codified on a Memorandum of Agreement, authored by the ANG and must be
renewed each fiscal year.
SECTION F – MAJCOM Unique Resource Requirements
NOTE: There are currently no MAJCOM unique resource requirements.
CFETP CEA
26
Attachment 1
Qualitative Requirements
THIS BLOCK FOR IDENTIFICATION PURPOSES ONLY
NAME OF TRAINEE
PRINTED NAME (Last, First Middle Initial)
INITIALS (Written)
SSAN
PRINTED NAME OF CERITFYING OFFICAL AND WRITTEN INITIALS
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
N/I
QUALITATIVE REQUIREMENTS
PROFICIENCY CODE KEY
SCALE
VALUE
DEFINITION: The Individual
TASK
PERFORMANCE
LEVELS
1
Can do simple parts of the task. Needs to be told or shown how to do most of the task.
(EXTREMELY LIMITED)
2
Can do most parts of the task. Needs help only on hardest parts. (PARTIALLY PROFICIENT)
3
Can do all parts of the task. Needs only a spot check of completed work. (COMPETENT)
4
Can do the complete task quickly and accurately. Can tell or show others how to do the task.
(HIGHLY PROFICIENT)
**TASK
KNOWLEDGE
LEVELS
a
Can name parts, tools, and simple facts about the task. (NOMENCLATURE)
b
Can determine step by step procedures for doing the task. (PROCEDURES)
c
Can identify why and when the task must be done and why each step is needed. (OPERATING
PRINCIPLES)
d
Can predict, isolate, and resolve problems about the task. (ADVANCED THEORY)
***SUBJECT
KNOWLEDGE
LEVELS
A
Can identify basic facts and terms about the subject. (FACTS)
B
Can identify relationship of basic facts and state general principles about the subject.
(PRINCIPLES)
C
Can analyze facts and principles and draw conclusions about the subject. (ANALYSIS)
D
Can evaluate conditions and make proper decisions about the subject. (EVALUATION)
EXPLANATIONS
**
A task knowledge scale value may be used alone or with a task performance scale value to define a level of knowledge for
a specific task. (Examples: b and 1b)
*** A subject knowledge scale value is used alone to define a level of knowledge for a subject not directly related to any
specific task, or for a subject common to several tasks.
- This mark is used alone instead of a scale value to show that no proficiency training is provided in the course.
x This mark is used alone in course columns to show that training is required but not given due to limitations in resources.
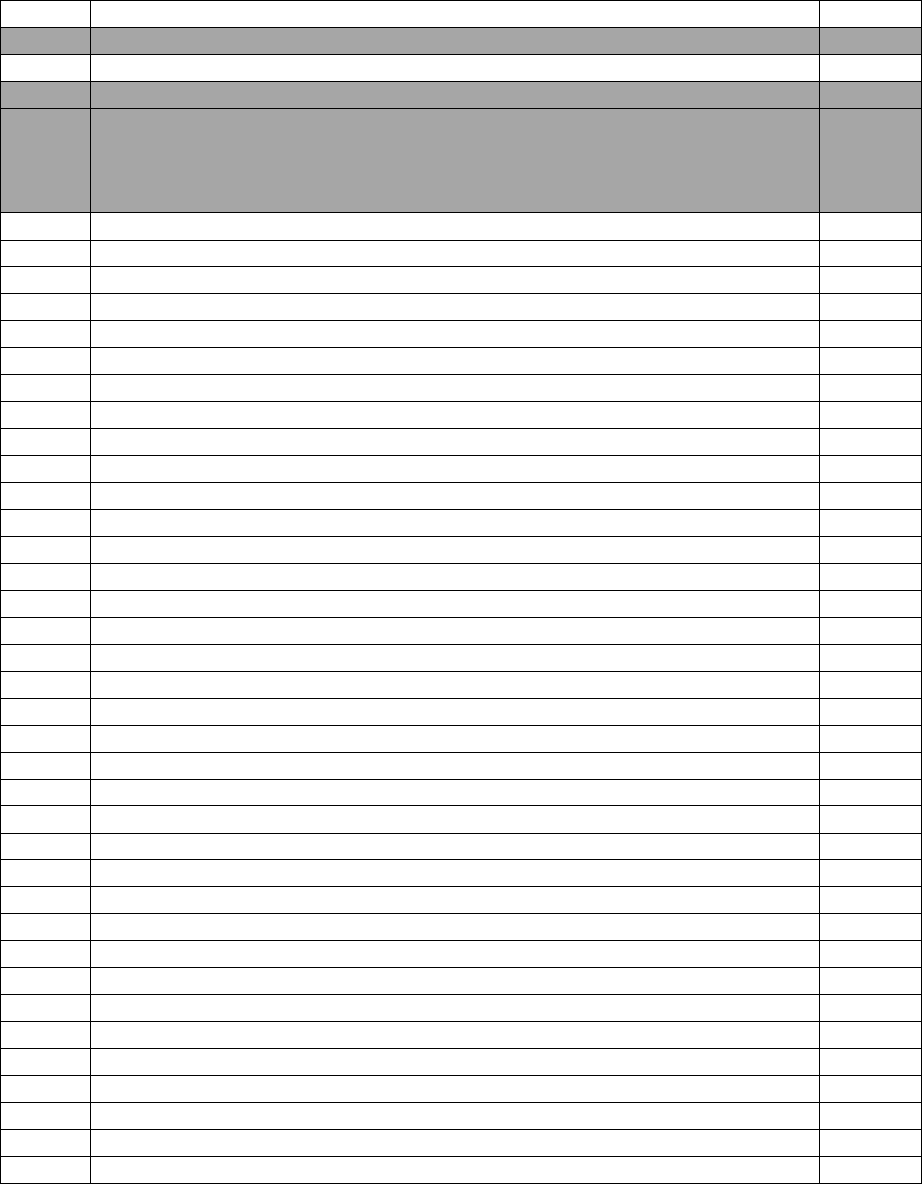
CFETP CEA
27
Attachment 2
Career Enlisted Aviator Fundamentals
Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References
Task
Standard
1
AEROSPACE PHYSIOLOGY
-
1.1
Aerospace Physiology Training
-
2
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR 101
-
References: CEA CFETP, T.O. 00-5-1, T.O.00-5-3, AFI 11-215, AFH1, AFMAN
11-202 V1/2/3, AFMAN 11-2XXX V1/2/3, DAFMAN 11-401, AFMAN 11-402,
AFMAN 11-403, AFMAN 11-290, DAFMAN 90-160, DAFMAN 90-161, AFI 90-
802
2.1
Electronic Flight Bag (EFB) and Publications
-
2.1.1
Orientation
-
2.1.2
Update EFB Applications and Data
2b
2.1.3
Navigate EFB Applications
2b
2.1.4
Air Force Technical Orders, Flight Manuals and Standard Publications
A
2.1.5
Navigate AF Technical Orders / Manuals
2b
2.2
Aviation History
-
2.2.1
Duties with 1A1XX
A
2.2.2
Career Progression within 1A1XX
A
2.2.3
Platforms and Crew Position Information
A
2.2.4
Airmanship
A
2.2.5
Aircrew Heritage
A
2.2.6
Air Force Doctrine
A
2.2.7
Joint Force Doctrine
A
2.3
Crew Resource Management (CRM)
-
2.3.1
Crew Resource Management
A
2.3.2
Risk Management
A
2.3.3
Aircrew Communications Terms & Definitions
A
2.4
Operational Structure
-
2.4.1
Career Enlisted Aviator Career Opportunities
A
2.4.2
Career Enlisted Aviator Qualifications
A
2.4.3
Standards and Evaluation Functions
A
2.4.4
Career Enlisted Aviator Missions
A
2.4.5
Career Enlisted Aviator Total Force Integration
A
2.4.6
Command Structure
A
2.4.7
MAJCOM Responsibilities
A
2.4.8
Joint Operations
A
2.5
Aircrew Responsibilities
A
2.5.1
Aviation Management
A
2.5.2
Aviation Service / Aeronautical Ratings / Badges
A
2.5.3
Incentives for Aviation Service
A
2.5.4
Flight Medicine Functions
A
2.5.5
Aircrew Member Responsibilities
A
2.5.6
Mentorship
A
2.6
Physiological Impacts
-
2.6.1
Human Performance
A

CFETP CEA
28
2.6.2
Impacts of Environmental Conditions
A
2.6.3
Nutrition
A
2.6.4
Injury Prevention
A
3
AIRCRAFT FUNDAMENTALS
-
References: T.O 1X-XXX-1, DAFI 91-225, AFMAN 11-290, DAFI 91-204, DAFI
10-706, JP 3-85
3.1
Aircraft Systems
-
3.1.1
Engines
B
3.1.2
Propeller Systems
A
3.1.3
Auxiliary Power Unit
A
3.1.4
Fuel
B
3.1.5
Bleed Air
B
3.1.6
Environmental
B
3.1.7
Oxygen
A
3.1.8
Electrical
B
3.1.9
Aircraft Sensors
A
3.1.10
Flight Instruments
A
3.1.11
Navigation
A
3.1.12
Aircraft Lighting
A
3.1.13
Communication
A
3.1.14
Hydraulic
B
3.1.15
Landing Gear
A
3.1.16
Brakes
A
3.1.17
Fire Detection
A
3.1.18
Fire Extinguishing
A
3.1.19
Aircraft Systems Integration
A
3.1.20
Electronic Warfare (EW) Principles
A
3.1.21
Aircraft Defensive Systems
A
3.1.22
Vertical Lift Rotors
A
3.1.23
Vertical Lift Transmission / Drive Systems
A
3.1.24
Crew Resource Management Related to Aircraft Systems
B
3.1.25
Aircraft Systems Mishap and Safety Investigations
B
3.1.26
Utilize Aircraft Systems Virtual Reality Modules
2b
3.2
Fundamentals of Flight
-
3.2.1
Aerodynamics
A
3.2.2
Flight Controls
B
3.2.3
Turbo-Prop Propulsion
A
3.2.4
Turbo-Fan Propulsion
A
3.2.5
Fixed Wing
A
3.2.6
Rotary Wing
A
3.2.7
Tiltrotor
A
3.2.8
Aircraft Aerodynamics Mishap and Safety Investigations
B
3.2.9
Utilize the Fundamentals of Flight Application
2b
4
WEIGHT & BALANCE/ TAKEOFF AND LANDING DATA (TOLD)
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-5, T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-2C-
XXX V3/Addenda A, T.O. 1-1B-50
4.1
Weight and Balance
-
4.1.1
Weight and Balance Concepts
A
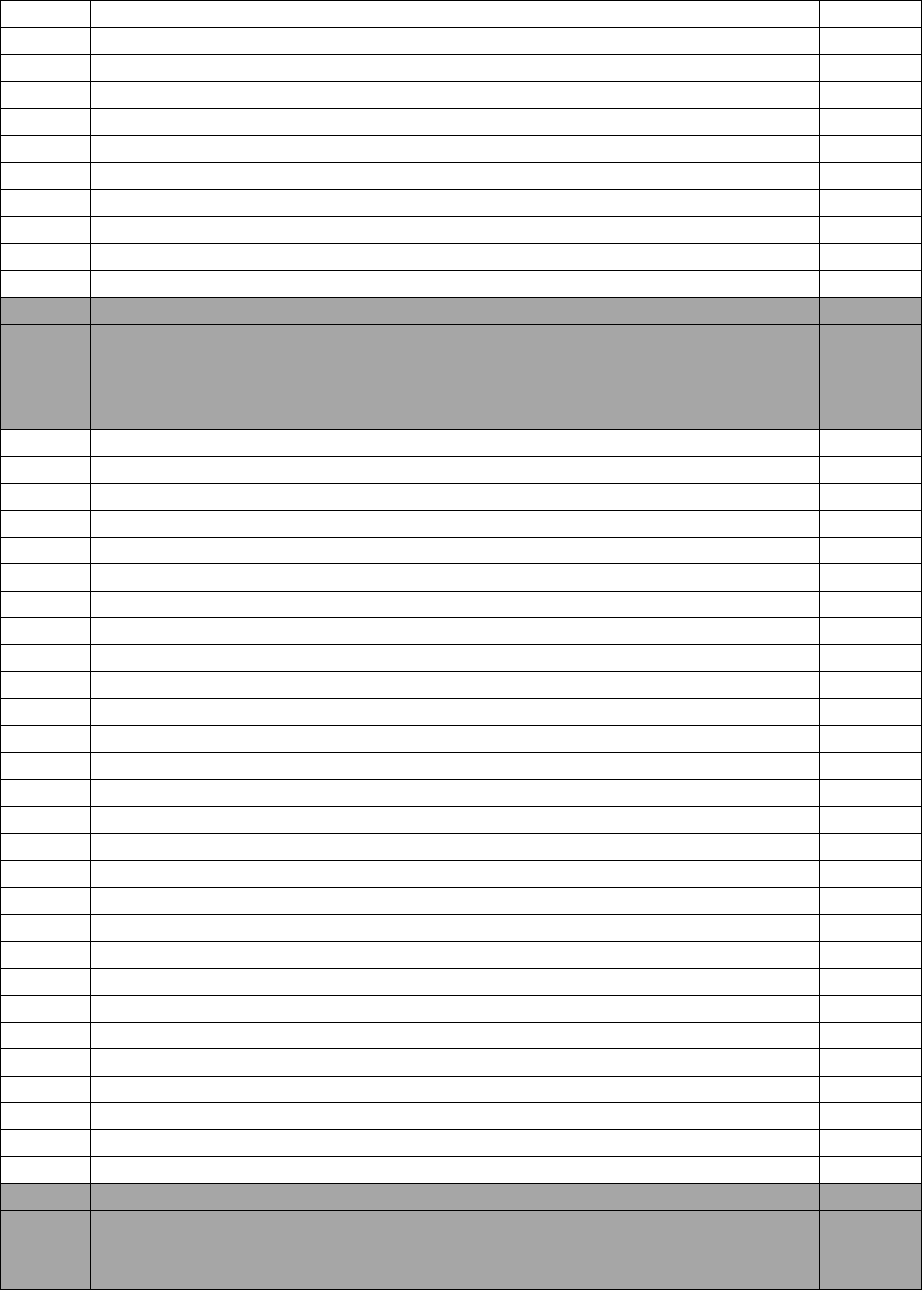
CFETP CEA
29
4.1.2
Effects of Weight and Balance
A
4.1.3
Apply Weight and Balance Formulas
2b
4.1.4
Weight and Balance Records
A
4.1.5
Complete Weight and Balance DD Form 365-4
2b
4.1.6
Tactical and Electronic Form F
A
4.2
Takeoff and Landing Data (TOLD)
-
4.2.1
Interpret Basic Performance Chart Data
2b
4.2.2
Takeoff Data
B
4.2.3
Landing Data
B
4.2.4
Cruise Data
B
4.2.5
Hover Data
B
5
AIRFIELD OPERATIONS
-
References: ACP 121, AFMAN 17-1302-O, AFI 13-207-O, AFI 10-701, T.O. 1X-
XXX-1, AFI 91-212, AFI 11-301V1, AFMAN 11-218, T.O. 00-20-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-
9, AFI 24-605 V2, JP 3-85, DOD Foreign Clearance Guide
5.1
Communication Principles
-
5.1.1
Radio Discipline
A
5.1.2
Internal Communication
A
5.1.3
External Communication
A
5.1.4
Emissions Control (EMCON)
A
5.1.5
Communication Security (COMSEC)
A
5.2
Security
-
5.2.1
Aircrew Security
A
5.2.2
Anti-Hijacking
A
5.2.3
Flightline Security Procedures
A
5.2.4
Operational Security (OPSEC)
A
5.3
Aircraft Hazards
-
5.3.1
Aviation Hazards
A
5.3.2
Emergency Equipment
A
5.3.3
Aircrew Flight Equipment
A
5.3.4
Emergency Egress Procedures
A
5.3.5
Marshalling
A
5.4
Aircraft Inspections
-
5.4.1
Pre-flight Inspections
A
5.4.2
Post-flight Inspections
A
5.4.3
AFTO IMT 781 Series Forms
A
5.4.4
Document Discrepancies on AFTO IMT 781 Series Forms
2b
5.5
Passengers PAX
-
5.5.1
Passenger Handling Procedures
A
5.5.2
Passenger and Crew Baggage
A
5.5.3
Brief Passengers / Troops
2b
5.5.4
Border Clearance Procedures/ Forms
A
5.5.5
Equipment Inventory Forms
A
6
MISSION PLANNING
-
References: T.O. 1X-XXX-1, AFH 11-203V1, AFH 11-203V2, AFI 11-208, FIH,
IRF SUP, AFI 11-290, DAFI 91-204, AFMAN 11-202-V3, AFMAN 11-218,
AFMAN 11-230
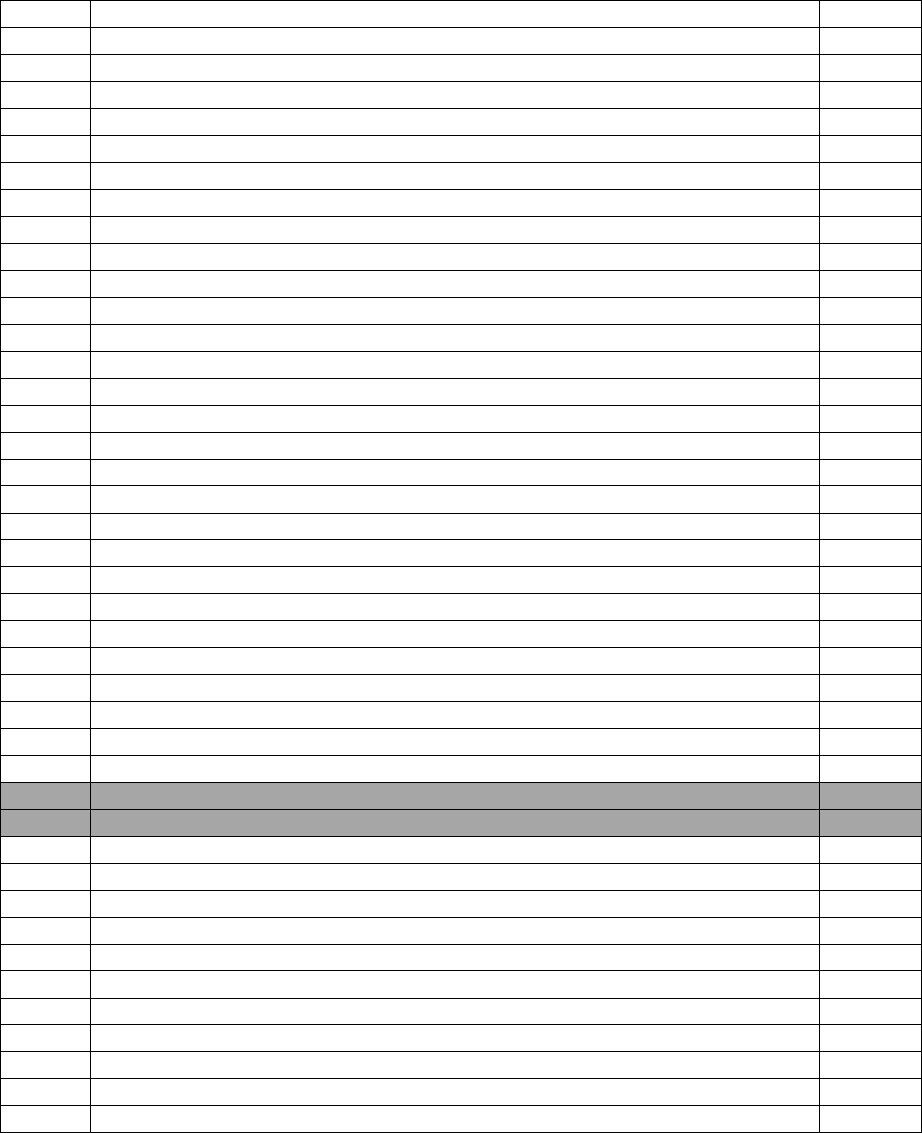
CFETP CEA
30
6.1
Weather
-
6.1.1
Atmosphere Principles
A
6.1.2
Physics Principles
A
6.1.3
Weather Report Interpretation
A
6.1.4
Extract Weather Report
2b
6.1.5
Interpret Weather Report
2b
6.1.6
Crew Resource Management related to Atmosphere and Weather
B
6.1.7
Weather Related Mishap and Safety Investigations
B
6.2
Navigation
-
6.2.1
NAVAID Identification and Principles
A
6.2.2
Extract Terminal and En-route NAVAID Information
2b
6.2.3
Interpret Terminal and En-route NAVAID Information
2b
6.2.4
Determine Position Orientation
2b
6.2.5
Terminal and En-route Procedures
A
6.2.6
Rendezvous Procedures
A
6.2.7
Determine Aircraft Position
2b
6.2.8
Determine Latitude / Longitude
2b
6.2.9
Extract General Navigation Information from Electronic Flight Bag (EFB)
2b
6.2.10
Interpret General Navigation Information from Electronic Flight Bag (EFB)
2b
6.3
Mission Planning
-
6.3.1
Mission Planning
A
6.3.2
Pre-Mission Briefings
A
6.3.3
Mission Responsibility
A
6.3.4
Mission Funds
A
6.3.5
Mission Forms
A
6.3.6
Complete Mission Forms
2b
6.3.7
Compute Resources Required for the Mission
2b
6.3.8
Perform Mission Planning
2b
6.3.9
Identify AFTO IMT 781 Series Forms
2b
7
NETWORK OPERATIONS
-
References: 1X-XXX-1
7.1
Network Operations
-
7.1.1
Network Fundamentals
A
7.1.2
Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance
A
7.1.3
Kinetic Operations
A
7.1.4
Multi-Domain Operations
A
7.1.5
Joint Environment
A
7.1.6
Threats
A
7.2
Final Testing
-
7.2.1
Complete BOLDFACE Test
2b
7.2.2
Complete Closed Book Test
2b
7.2.3
Complete Open Book Test
2b
CFETP CEA
31
Attachment 3
1A1X2- Mobility Force Aviator
Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References
Task
Standard
1
AEROSPACE PHYSIOLOGY
-
2
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR 101
-
3
AIRCRAFT FUNDAMENTALS
-
4
WEIGHT & BALANCE/ TAKEOFF AND LANDING DATA (TOLD)
-
5
AIRFIELD OPERATIONS
-
6
MISSION PLANNING
-
7
NETWORK OPERATIONS
-
8
CARGO LOAD PLANNING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-2CXXX V3 Addenda A
8.1
CARGO LOAD PLANNING
-
8.1.1
Vehicle Center of Gravity Concepts
A
8.1.2
Compute Vehicle Center of Gravity
2b
8.1.3
Concepts of Load Planning
A
8.1.4
Apply Formulas for Load Planning
2b
8.1.5
Validate Load Plans
2b
8.1.6
Compute Cargo Load Plan
2b
9
CARGO LOADING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-218, AFI 90-802
9.1
CARGO LOADING
-
9.1.1
Apply Risk Management related to Cargo Loading
2b
9.1.2
Conduct Before Loading Checklist
2b
9.1.3
Direct Loading of Palletized Cargo with a K-loader
2b
9.1.4
Direct Loading of Palletized Cargo with a Forklift
2b
9.1.5
Conduct After Loading Checklist
2b
9.1.6
Direct Offloading of Palletized Cargo with a K-loader
2b
9.1.7
Direct Offloading of Palletized Cargo with a Forklift
2b
9.1.8
Direct Loading of Self-Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
9.1.9
Direct Offloading of Self- Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
9.1.10
Marshalling Material Handling Equipment (MHE)
2b
10
CARGO RESTRAINT AND HANDLING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-2CXXX V3 Addenda A,
AFMAN 24-604, AFI 24-605 V2
10.1
CARGO RESTRAINT
-
10.1.1
Concepts of Restraint
A
10.1.2
Utilize Aircraft Tiedown Equipment
2b
10.1.3
Perform Restraint of Self- Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
10.1.4
Compute Restraint Criteria
2b
10.1.5
Area and Pounds Per Square Inch
A
10.1.6
Shoring Requirements
A
10.1.7
Compute Area and Pounds Per Square Inch
2b
10.1.8
Compute Shoring Requirements
2b
10.2
CARGO HANDLING
-
10.2.1
Cargo Documentation
A

CFETP CEA
32
10.2.2
Special Handling Procedures
A
10.2.3
Hazardous Cargo (HAZMAT) (AFMAN 24-604)
A
10.2.4
Determine Segregation / Compatibility of HAZMAT
2b
10.2.5
Cargo Inspection Procedures
A
10.2.6
Inspect Palletized Cargo
2b
10.2.7
Inspect Rolling Stock
2b
10.2.8
Safety Requirements
A
10.2.9
Cargo Loading Aids and Materiel Handling Equipment
A
10.2.10
Cargo Loading Checklist
A
10.2.11
Cargo Offloading Checklist
A
11
MOBILITY FORCE AVIATOR 101
-
References: AFMAN 11-202V1, AFI 11-401, T.O. 1C-XXX-1, ATP 3.3.4.2
11.1
MOBILITY FORCE AVIATOR INFORMATION
-
11.1.1
Mobility Force Aviator Duties and Qualifications
A
11.2
AIR REFUELING INFORMATION
-
11.2.1
Boom & Drogue Characteristics
A
11.2.2
Boom Aerodynamic Effects
A
11.2.3
Aerial Refueling Systems Components
B
11.2.4
Tanker Communications
A
11.3
AERIAL REFUELING PROCEDURES
-
11.3.1
Tanker Rendezvous
A
11.3.2
Air Refueling Limitations and Specifications
A
11.3.3
Air-to-Air Refueling Procedures
b
12
MOBILITY FORCE AVIATOR MISSION PLANNING
-
12.1
MOBILITY AVIATOR MISSION PLANNING
-
12.1.1
Complete Mobility Aviator Mission Planning
2b
CFETP CEA
33
Attachment 4
1A1X3- Special Missions Aviator
Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References
Task
Standard
1
AEROSPACE PHYSIOLOGY
-
2
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR 101
-
3
AIRCRAFT FUNDAMENTALS
-
4
WEIGHT & BALANCE/ TAKEOFF AND LANDING DATA (TOLD)
-
5
AIRFIELD OPERATIONS
-
6
MISSION PLANNING
-
7
NETWORK OPERATIONS
-
8
CARGO LOAD PLANNING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-2CXXX V3 Addenda A
8.1
Cargo Load Planning
-
8.1.1
Vehicle Center of Gravity Concepts
A
8.1.2
Compute Vehicle Center of Gravity
2b
8.1.3
Concepts of Load Planning
A
8.1.4
Apply Formulas for Load Planning
2b
8.1.5
Validate Load Plans
2b
8.1.6
Compute Cargo Load Plan
2b
9
CARGO LOADING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-218, AFI 90-802
9.1
Cargo Loading
-
9.1.1
Apply Risk Management related to Cargo Loading
2b
9.1.2
Conduct Before Loading Checklist
2b
9.1.3
Direct Loading of Palletized Cargo with a K-loader
2b
9.1.4
Direct Loading of Palletized Cargo with a Forklift
2b
9.1.5
Conduct After Loading Cargo Checklist
2b
9.1.6
Direct Offloading of Palletized Cargo with a K-loader
2b
9.1.7
Direct Offloading of Palletized Cargo with a Forklift
2b
9.1.8
Direct Loading of Self-Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
9.1.9
Direct Offloading of Self- Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
9.1.10
Marshalling Material Handling Equipment (MHE)
2b
10
CARGO RESTRAINT AND HANDLING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, T.O. 1C-XXX-9, AFMAN 11-2CXXX V3 Addenda A,
AFMAN 24-604, AFI 24-605 V2
10.1
Cargo Restraint
-
10.1.1
Concepts of Restraint
A
10.1.2
Utilize Aircraft Tiedown Equipment
2b
10.1.3
Perform Restraint of Self- Propelled Tactical Military Vehicle with Tiedown Points
2b
10.1.4
Compute Restraint Criteria
2b
10.1.5
Area and Pounds Per Square Inch
A
10.1.6
Shoring Requirements
A
10.1.7
Compute Area and Pounds Per Square Inch
2b
10.1.8
Compute Shoring Requirements
2b
10.2
Cargo Handling
-
10.2.1
Cargo Documentation
A
10.2.2
Special Handling Procedures
A
CFETP CEA
34
10.2.3
Hazardous Cargo (HAZMAT) (AFMAN 24-604)
A
10.2.4
Determine Segregation/Compatibility of HAZMAT
2b
10.2.5
Cargo Inspection Procedures
A
10.2.6
Inspect Palletized Cargo
2b
10.2.7
Inspect Rolling Stock
2b
10.2.8
Safety Requirements
A
10.2.9
Cargo Loading Aids and Material Handling Equipment
A
10.2.10
Cargo Loading Checklist
A
10.2.11
Cargo Offloading Checklist
A
11
SPECIAL MISSION AVIATOR 101
-
References: CFETP, AFECD, 1C-XXX-1
11.1
Special Mission Aviator Information
-
11.1.1
Special Mission Aviator Duties and Qualifications
A
11.1.2
Special Missions Aviator Mission Taskings
A
11.2
Aircraft Systems/Equipment
-
11.2.1
Rotor Systems
B
11.2.2
Transmission / Drive Systems
B
11.2.3
Prop-Rotor Systems
B
11.3
Aerodynamics
-
11.3.1
Rotary Wing
B
11.3.2
Tiltrotor
B
12
NAVIGATION/MISSION PLANNING
-
References: AFTTP 3-3
12.1
Navigation
-
12.1.1
Mission Planning/ Form 70
B
12.1.2
Determine UTM/ MGRS
2b
13
WEAPONS AND TACTICS
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, AFMAN 91-201, AFTTP 3-3, T.O. 1C-XXX-1-43
13.1
Aircraft Weapons Systems Principles of Operation
-
13.1.1
Weapon Safety
A
13.1.2
Ammunition / Ballistic Principles
A
13.1.3
Theory of Operations
A
13.1.4
Fixed Wing Armament
A
13.1.5
Rotary Wing Armament
A
13.1.6
Tools
A
13.1.7
Kill Chain/ROE/LOAC/JFIRE/JP3-50
A
13.2
Alternate Insertion/Extraction (AIE) Operations
-
13.2.1
Principles of Operation
A
13.2.2
System Components
A
13.2.3
Inspection
A
CFETP CEA
35
Attachment 5
1A1X4- Multi-domain Operations Aviator
Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References
Task
Standard
1
AEROSPACE PHYSIOLOGY
-
2
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR 101
-
3
AIRCRAFT FUNDAMENTALS
-
4
WEIGHT & BALANCE/ TAKEOFF AND LANDING DATA (TOLD)
-
5
AIRFIELD OPERATIONS
-
6
MISSION PLANNING
-
7
NETWORK OPERATIONS
-
8
AIRCRAFT NETWORKING
-
References: T.O. 31-1-141 Series, T.O. 1E-3A-1, T.O. 1C-135(RC)(I)-1, T.O. 1Q-
9(M)A-1
8.1
Basic Electronics
A
8.2
Computers
B
8.2.1
Computer Systems (hardware)
B
8.2.2
Computer Networking
B
8.2.3
Perform Computer Networking/Troubleshooting
2b
8.2.4
Computer Network Management / Network Security
B
9
ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM AND SYSTEMS
-
References: T.O. 31-1-141 Series AFH 11-203V1
9.1
Electromagnetic Spectrum
A
9.2
Sensor Performance / Military means of sensing
B
9.3
Wave Propagation
A
9.4
Weather Effects on Sensor Systems
A
9.5
Radar Theory, Components & Range Equation
A
9.6
Control of Electromagnetic Spectrum
A
9.7
Divisions of Electromagnetic Warfare
A
10
WORKSTATION DISPLAYS AND INTERPRETATION
-
References: AFTTP 3-3 AWACS, AFTTP 3-3 MQ-9, AFTTP 3-3 RQ-4
10.1
Systems Optimization
A
10.2
Target Acquisition Techniques / Scan types
A
10.3
Determine Aircraft/Target Orientation
2b
10.4
Interpret Displays & Data
2b
11
GEOSPATIAL REFERENCE SYSTEMS
-
References: AFTTP 3-3 AWACS, AFTTP 3-3 MQ-9, AFTTP 3-3 RQ-4
11.1
Types of Aviation Maps and Charts
A
11.2
Military Grid Reference System
A
11.3
Latitude/Longitude
A
11.4
Bearing and Range
A
11.5
Global Area Reference System
A
12
COMMUNICATIONS
-
References: AFTTP 3-3 AWACS, AFTTP 3-3 MQ-9, AFTTP 3-3 RQ-4, T.O. 1E-3A-1,
T.O. 1C-135(RC)(I)-1, T.O. 1Q-9(M)A-1, AFTTP 3-2.5 Brevity
CFETP CEA
36
12.1
Radio Telephone Procedures
B
12.2
Perform Radio Communications and Crew Interaction
2b
12.3
Perform Methods/Types of Calls
2b
12.4
Utilize Tactical Chat
2b
12.5
Radio Frequency Bands
A
12.6
Antenna Principles and Types
A
12.7
Anti Jam Systems
A
12.8
Secure/Unsecure Communications
A
12.9
Situational Awareness Data Links
A
12.10
Tactical Data Links
A
12.11
Video Data Links
A
12.12
Voice Tell
A
12.13
Control Data Links
A
12.14
Beyond Line of Sight Operations
A
12.15
Line of Sight Operation
A
12.16
Data Link Encryption
A
12.17
Identify Friend or Foe (IFF) System / Concepts
A
13
OPERATIONS IN CONTESTED ENVIRONMENT
-
References: T.O. 1E-8C-43-1-1, T.O. 1E-3A-43-1-1, AFI 33-201, AFI 10-706 AFH 11-
203 V1, ACP 121, 125, 131, 135, 167 (J)
13.1
Introduction to Threats
A
13.2
IADS Effectiveness/Risk Management
A
13.3
Signal to Noise Ratio
A
13.4
Radar Cross-section
A
13.5
Radar Plots
A
13.6
Decibels
A
13.7
Signature Management
A
13.8
Spike Management
A
13.9
Avoidance Techniques
A
13.10
Interception (Enemy Air-to Air)
A
14
MOA MISSION EMPLOYMENT
References: AFTTP 3-3 AWACS, AFTTP 3-3 MQ-9, AFTTP 3-3 RQ-4, AFTTP 3-3
RC-135, AFTTP 3-3
14.1
Mission Sets
B
14.2
Mission Taskings
A
14.3
Airspace Control
A
14.4
Coordinate / Deconflict Airspace
2b
14.5
Threat Reduction
B
14.6
Mission Planning
2b
14.7
Mission Execution / CRM Application
2b
14.8
Perform Crew Briefings
2b
CFETP CEA
37
Attachment 6
1A1X8- Executive Mission Aviator
Tasks, Knowledge, and Technical References
Task
Standard
1
AEROSPACE PHYSIOLOGY
-
2
CAREER ENLISTED AVIATOR 101
-
3
AIRCRAFT FUNDAMENTALS
-
4
WEIGHT & BALANCE/ TAKEOFF AND LANDING DATA (TOLD)
-
5
AIRFIELD OPERATIONS
-
6
MISSION PLANNING
-
7
NETWORK OPERATIONS
-
8
EXECUTIVE MISSION AVIATOR 101
-
References: CEA CFETP, AFH1, AFECD, AFMAN 11-2E-XXX V1, 1X-XXX-1,
T.O. 1X-XXX-1-1, AFH 11-203 V1, ACP 121/125/131/135/167(J), T.O. 1C-XXX-1
8.1
Executive Mission Aviator Information
-
8.1.1
Executive Mission Aviator Duties and Qualifications
A
8.2
Distinguished Visitor Aircraft
-
8.2.1
Aircraft Orientation
A
8.3
Computers
-
8.3.1
Computer Systems
B
8.3.2
Computer Networking
B
8.3.3
Perform Computer Networking/ Troubleshooting
2b
8.4
Communication Systems
-
8.4.1
Systems
B
8.4.2
Voice Tell
A
8.4.3
Effects of Weather
A
8.4.4
Anti-Jam Systems
A
8.4.5
Radio/ Telephone Procedures
A
8.4.6
Perform Standard Radio/ Telephone Procedures
2b
8.5
Electronics
-
8.5.1
Basic Electronics
A
8.5.2
Wave Propagation
A
8.5.3
Cooling Systems
A
9
PASSENGER/ MEAL PROCEDURES
-
References: AFI 34-1201, DAFI 36-2903, AFMAN 11-2EA V3, Assorted Cookbooks,
Assorted Culinary Textbooks, Assorted Online Culinary Resource Sites
9.1
General Activities
-
9.1.1
Manners/Etiquette/Protocol
A
9.2
Meal Activities
-
9.2.1
Mission Menus
A
9.2.2
Prepare Mission Menus
2b
9.2.3
Create Menu Options
2b
9.2.4
Plan Menus According to Passenger Count
2b
9.2.5
Ensure Menus Correlate with Passenger Likes/Dislikes List
2b
9.2.6
Shopping Requirements
A
9.2.7
Requirements for Wet Ice/Dry Ice/Potable Water/Lavatory at each Ground Stop with
Appropriate Agencies
A
9.2.8
Complete Pre-Mission Shopping Requirements
2b
CFETP CEA
38
9.2.9
Transportation for En-Route Meal Shopping Trips with Other Agencies
A
9.2.10
Passengers with Special Dietary Considerations
A
9.2.11
Acquire Food and Beverages During En-Route Shopping Trips
A
9.2.12
Meals
B
9.2.13
Prepare Meals
2b
9.2.14
Demonstrate Basic Culinary Skills
2b
9.2.15
Food Groups/Dietary Restrictions/Special Diets/Selecting Food Items
A
9.2.16
Food Safety/Sanitation
B
9.2.17
Demonstrate Food Safety and Sanitation
2b
9.2.18
Food Storage
A
9.2.19
Food Preservation Techniques
A
9.2.20
Pack Coolers/Gray Ghosts
2b
9.2.21
Prepare/Organize/Store Food In Accordance with Applicable Health/Safety Codes
2b
9.2.22
Label Food Items For Storage
2b
9.2.23
Inventory/Store Food/Fleet Items
2b
9.2.24
Perform Overnight Food Storage to Include Refrigeration and Freezing
2b
9.2.25
Galley Equipment
A
9.2.26
Operate Galley Equipment
2b
10
MISSION PLANNING
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, Foreign Clearance Guide, AFMAN 11-2EA V3
10.1
Mission Planning
-
10.1.1
Mission Responsibilities
A
10.1.2
Fleet Supplies
A
10.1.3
Manually Load all Mission required items
A
10.1.4
Coordinate Aircraft Loading with Supporting Agencies
2b
10.1.5
Acquire/Review Mission Itineraries
2b
10.1.6
Itinerary Changes with Aircraft Commanders (ACs)/Mission Contacts
2b
10.1.7
Conduct Pre-Mission Planning with Appropriate Agencies
A
10.1.8
Coordinate Pre-Mission Tasks with Crew
2b
10.1.9
Perform Advance Meal Preparations
2b
10.1.10
Assign/Delegate Tasks to Crew Members
2b
10.1.11
Catered Meals with Appropriate Agencies
A
10.1.12
Coordinate Wet/Dry Ice Acquisition En-route for Multi-Day RONs with Appropriate
Agencies
A
10.1.13
Mission Expense Reports
A
10.2
Post Mission
-
10.2.1
Inventory Aircraft Supplies Post- Mission
2b
10.2.2
Perform End Of Mission Aircraft Fleet/Inventory
2b
10.2.3
Complete Post-Mission Debriefs
2b
10.2.4
Order/Replenish Fleet Supplies
2b
11
EMERGENCY PROCEDURES
-
References: T.O. 1C-XXX-1, AFMAN 11-2EA V3
11.1
Emergency Procedures & Safety
-
11.1.1
Perform Aircraft Inspection
2b
11.1.2
Secure Aircraft Cabin
2b
11.1.3
Basic First Aid Familiarization
A
11.1.4
Perform Announcements
2b
11.1.5
Emergency Procedures
2b
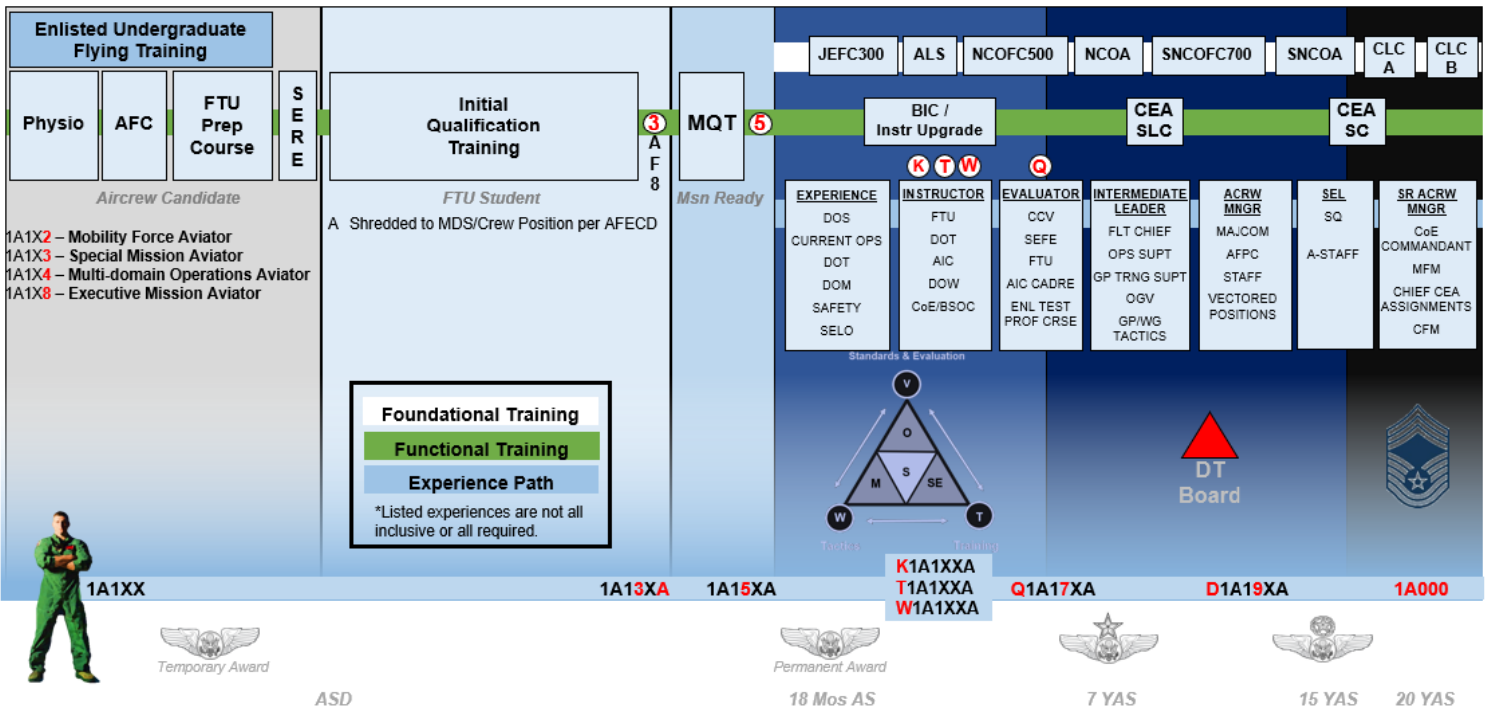
39
CFETP CEA
Figure 1. CEA Career Path
